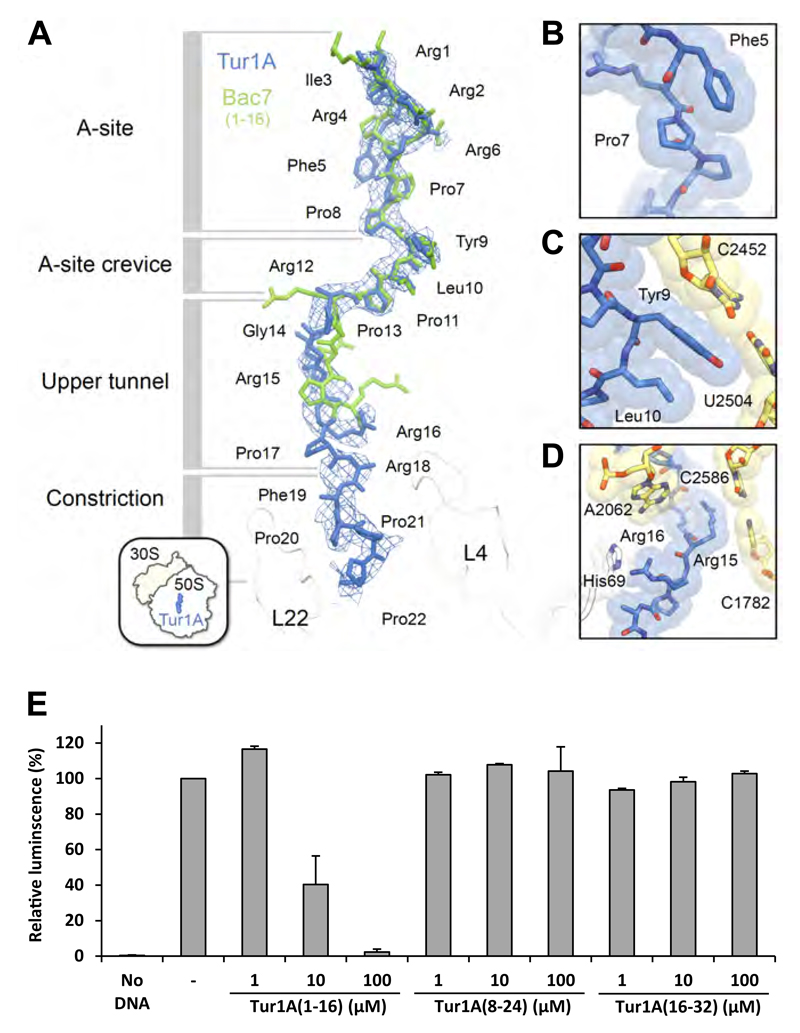
Figure 6. Binding site of Tur1A on the ribosome.
(A) The structure of Tur1A(1-22) (blue) is superimposed with that of Bac7(1-16) (green) (Seefeldt et al., 2016) and density contoured at +2.5 σ of a minimally-biased Fo-Fc map shows the location of the Tur1A peptide (blue mesh). The density was trimmed using the carve function in Pymol, with a 3 Å cutoff. The various sections of the nascent polypeptide exit tunnel are labelled, as well as ribosomal proteins L4 and L22 (white). (B-D) detailed view of (B) Phe5 stacking on Pro7 of Tur1A, (C) Tyr9 of Tur1A stacking on the C2452-U2504 basepair of the 23S rRNA, and (D) Arg15 and Arg16 of Tur1A stacking on basepair C2586-C1782 of the 23S rRNA and His69 of L4, respectively. (E) Luciferase activity after in vitro E. coli coupled transcription/translation assays performed in presence of Tur1A(1-16), Tur1A(8-24) or Tur1A(16-32). Reactions were performed in the absence (-) or presence of increasing concentrations of peptides. The luminescence resulting of reactions performed in the absence of peptides was normalized to 100%. Reactions lacking DNA template (No DNA) were performed as negative controls. The error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean from two independent experiments.