Figure 1.
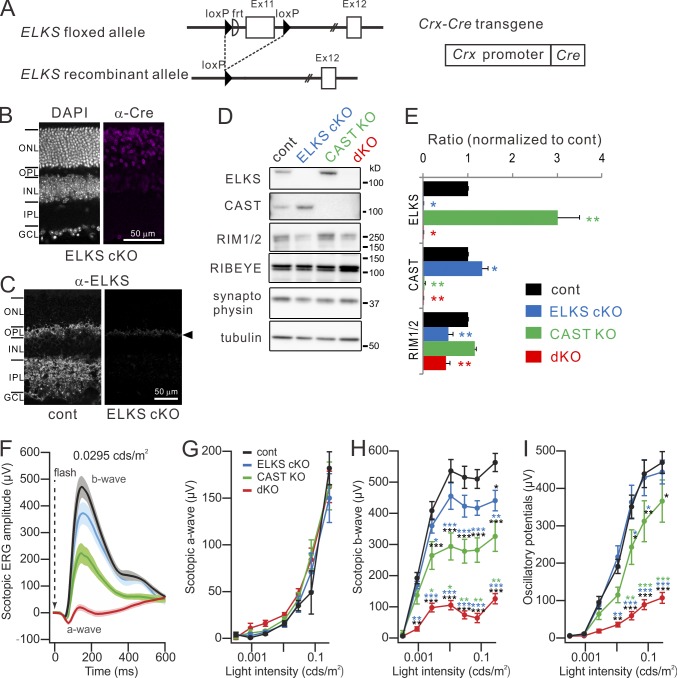
Genetic ablation of CAST and ELKS in the retina elicits impaired photoreceptor neurotransmission. (A) The ELKS flox allele contains two loxP sequences flanking exon 11 of mouse ELKS. Conditional ablation of ELKS was mediated by crossing ELKS flox mice with Crx-Cre mice. (B and C) Immunohistochemistry for Cre expression and subsequent depletion of ELKS from ELKS cKO retina. (C) ELKS distribution in both OPL and IPL is depleted, although a slight background signal is detected at the OPL (arrowhead). GCL, ganglion cell layer. Bars, 50 µm. (D and E) Western blotting of adult (9–12-wk-old) retinal homogenates of mutant mice with indicated antibodies. (E) ELKS expression (n = 6) is increased in the CAST KO and, conversely, CAST expression (n = 4) is enhanced in the ELKS cKO. RIM1/2 expression (n = 3) is reduced by ∼50% in ELKS cKO and dKO mice; mean ± SEM; asterisks indicate statistical comparison to control. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey test). (F–I) Scotopic ERG responses recorded from control (n = 7), ELKS cKO (n = 6), CAST KO (n = 7), and dKO (n = 7). Scotopic b-waves (H), indicating downstream BC activity, and oscillatory potentials (I) are significantly impaired in CAST KO, and even more dramatically in dKO, while a-waves (G), indicating phototransduction, remained unaffected. Colored asterisks indicate statistical comparison to the respectively colored genotypes and statistical significance. mean ± SEM; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (two-way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey test).