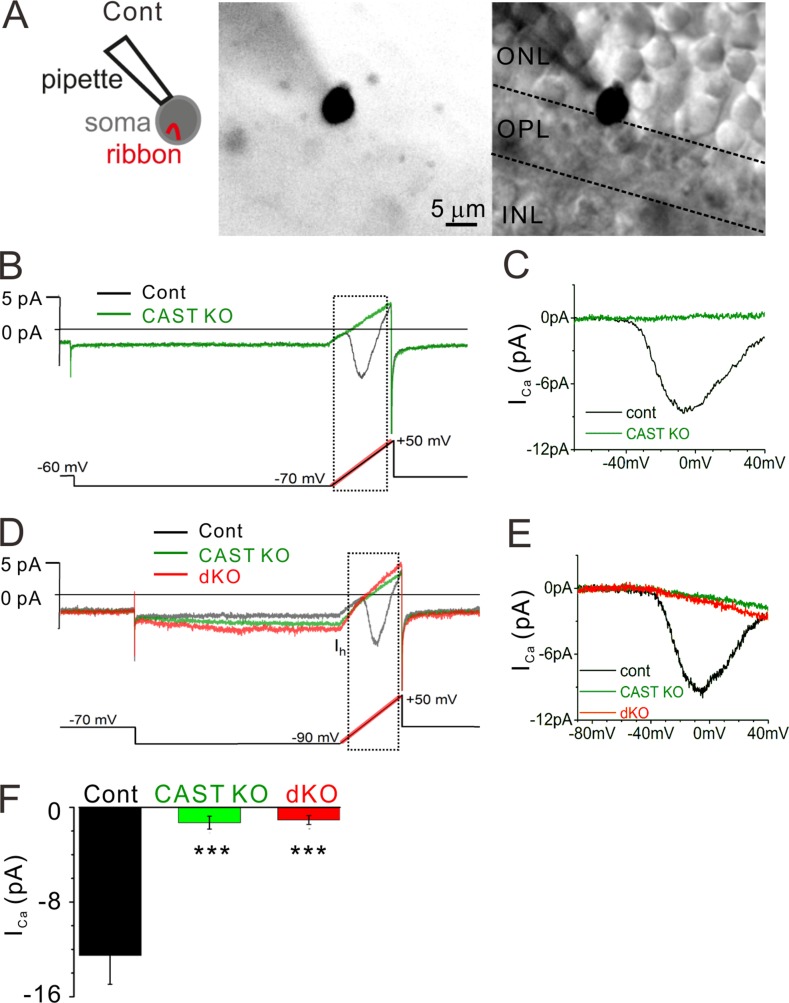
Figure 5.
ICa is drastically reduced in CAST KO and dKO rod photoreceptors. (A) Representative images of a recording made from a soma located at the ONL–OPL border, where the ribbon is contained in the soma compartment. The cell is filled with an Alexa Fluor 488 via recording pipette. Bars, 5 µm. (B and C) Control rod current trace (black line) exhibits the current-voltage (I-V) behavior for rod voltage-dependent CaV1.4 channels (recording from the cell that is presented in A). The voltage protocol is indicated at the bottom, and the ramp portion is highlighted in red. The current response to the voltage ramp (indicated by dashed square) is leak subtracted and presented in C. In contrast to the control, the CAST KO trace (green line) lacks an inward current. (D and E) The voltage protocol further tests the excitability of the cells by stepping from −70 to −90 mV to activate a Ih. While all genotypes showed inward Ih, CAST KO and dKO mice exhibited no signs of ICa. Current traces are presented after 1 kHz low-pass filtering. (F) The average peak amplitudes including the ramps starting at −70 and −90 mV were drastically reduced in CAST KO and dKO mice. In contrast, there were no significant differences between CAST KO and dKO mice (P < 0.7), mean ± SEM. control, n = 9 cells from seven mice; CAST KO, n = 8 cells from seven mice; dKO, n = 16 cells from 11 mice; ***, P < 0.001 (two-sided Student’s t test).