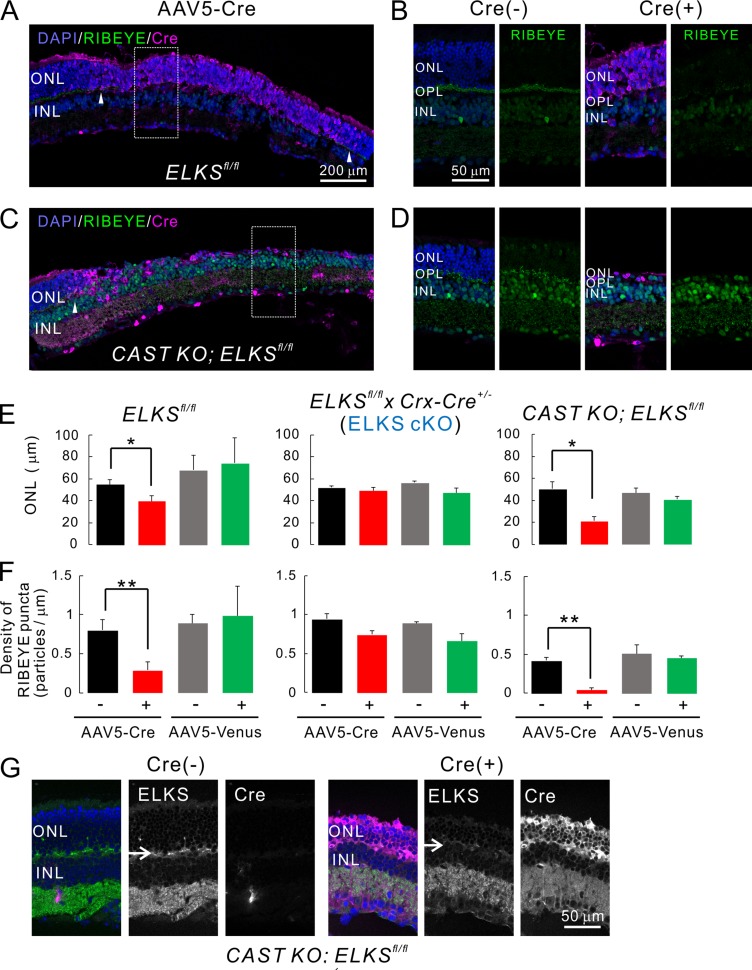
Figure 6.
Acute, AAV-mediated, ELKS depletion in photoreceptors induces photoreceptor degeneration. (A–D) Acute induction of ELKS cKO and dKO via AAV5-CAGGS-nCre. Subretinal injection of AAV5 produces mosaic Cre expression in the retina (Cre[+], indicated by arrowheads in A and C). (B and D) Immunolabeling of RIBEYE (green) in the OPL is reduced in the Cre-positive area (expansion of area indicated by white rectangle in A and C), when directly compared with adjacent Cre-negative regions (Cre[−] in B and D). Bars, 200 µm in A and C, 50 µm in B and D. (E and F) Quantitative analysis of ONL thickness and RIBEYE density. In ELKSfl/fl and CAST KO; ELKSfl/fl mice, ONL thickness (E) and RIBEYE density (F) are significantly decreased in Cre-positive regions, although Venus expression does not affect these parameters. Importantly, acute Cre expression in ELKSfl/fl x Crx-Cre+/− (ELKS cKO) mice affects neither ONL thickness nor RIBEYE density, indicating a CAST/ELKS-dependent mechanism as the underlying cause; mean ± SEM. ONL: ELKSfl/fl; Cre (n = 5 mice), Venus (n = 2), ELKSfl/fl x Crx-Cre+/−; Cre (n = 3), Venus (n = 3), CAST KO; ELKSfl/fl; Cre (n = 3), and Venus (n = 3). RIBEYE: ELKSfl/fl; Cre (n = 5), Venus (n = 2), ELKSfl/fl x Crx-Cre+/−; Cre (n = 3), Venus (n = 2), CAST KO; ELKSfl/fl; Cre (n = 4), and Venus (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (two-sided Student’s t test). (G) Ablation of ELKS in the OPL in CAST KO; ELKSfl/fl Cre (+) retina (arrows). Bar, 50 µm.