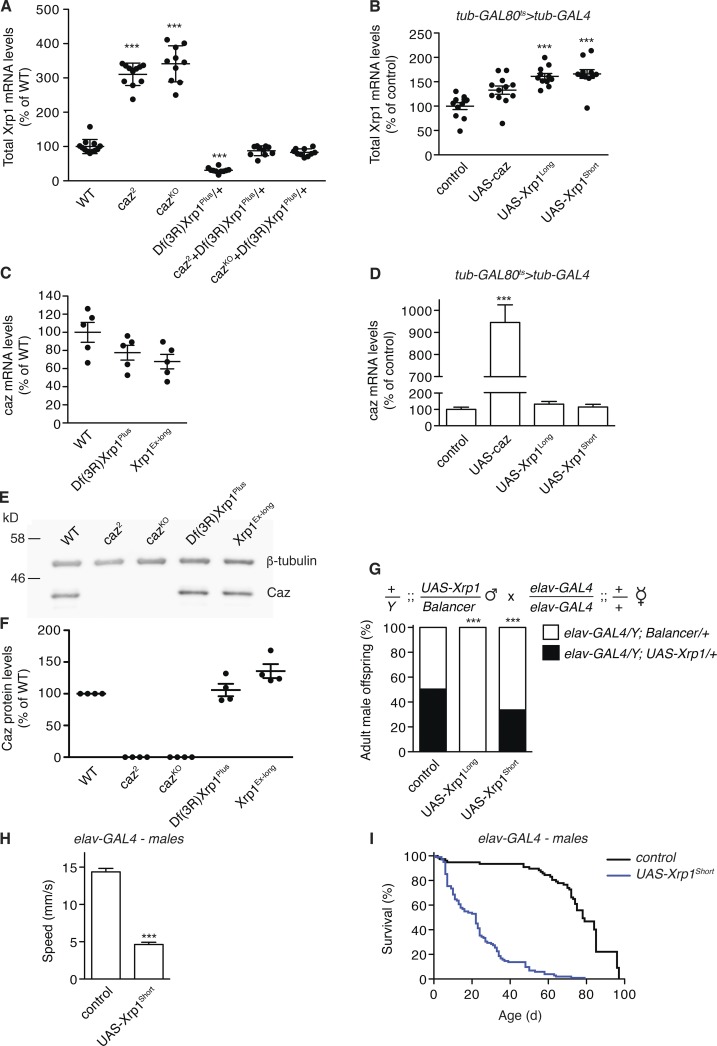
Figure 3. .
Xrp1 expression is up-regulated in caz mutants, and selective neuronal Xrp1 overexpression phenocopies caz mutant phenotypes. (A) Xrp1 transcript levels as determined by qPCR on CNS of WT, caz mutant, Xrp1 heterozygous, and caz mutant Xrp1 heterozygous larvae. n = 10. (B) Xrp1 transcript levels in heads of adult male flies that ubiquitously (tub-GAL4) overexpress Caz, Xrp1Long, Xrp1Short, or no transgene (control) from the adult stage onwards. n = 10. (C) Caz transcript levels in larval CNS of WT and two Xrp1 mutants. n = 10. (D) Caz transcript levels in heads of adult male flies that ubiquitously overexpress caz, Xrp1Long, Xrp1Short, or no transgene (control) from the adult stage onwards. n = 10. ***, P < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA. (E) Representative Western blot to evaluate Caz protein levels in larval CNS from WT, caz mutants, and Xrp1 mutants. β-tubulin was used as loading control. (F) Quantification of Caz protein levels relative to β-tubulin. n = 5. P = NS; one-way ANOVA. (G) Frequency of adult male offspring from the indicated cross. n > 111 per genotype. ***, P < 0.0005; χ2 test. (H) Average climbing speed of adult male flies selectively overexpressing Xrp1Short in neurons (elav-GAL4) as compared with driver-only controls. n > 100 per genotype. ***, P < 10−9; Mann-Whitney test. (I) Life span of male flies selectively overexpressing Xrp1Short in neurons (elav-GAL4) as compared with driver-only controls. n = 77–102. All graphs display mean ± SEM.