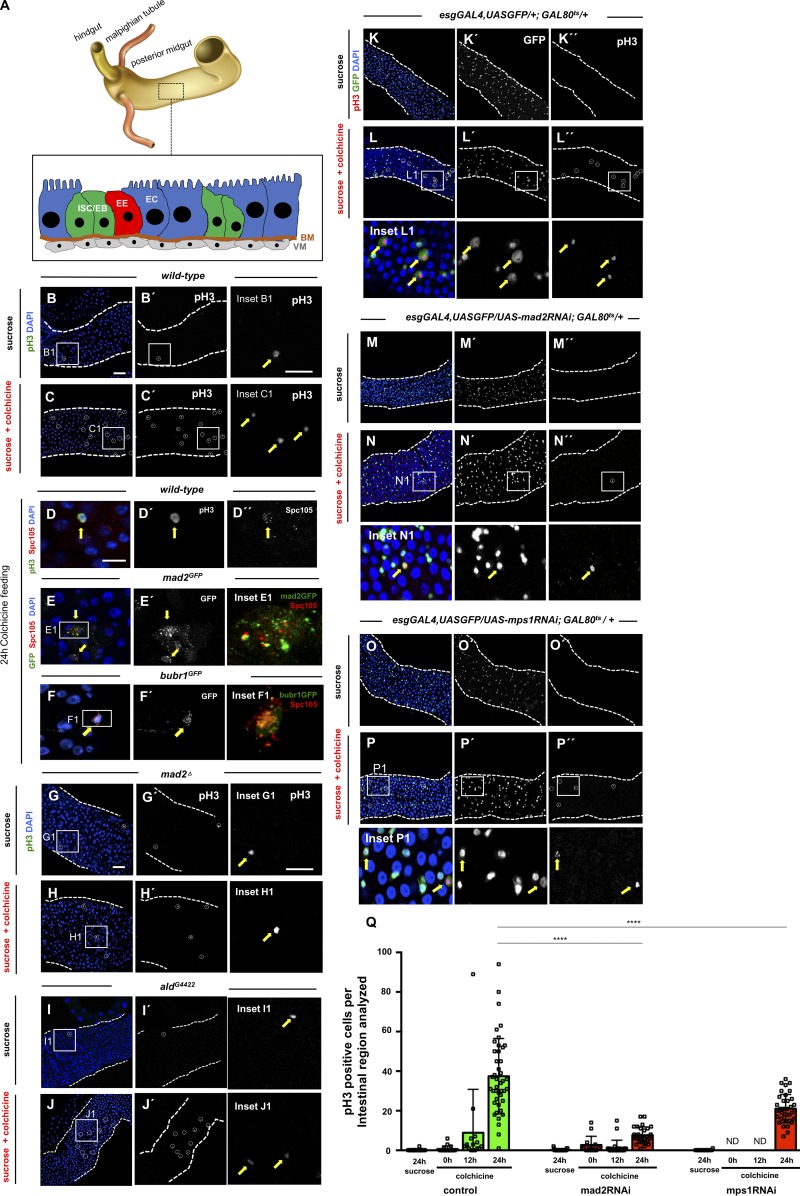
Figure 1.
ISCs are SAC competent. (A) Anatomical organization of the Drosophila intestine and schematic representation of different cell types of the posterior midgut. ISCs/EBs are the progenitor cells and are found in close association with basement membrane (BM) and visceral muscle (VM). Differentiated cell types include EE cells and absorptive ECs. (B) Mitotic cells labeled with pH3 (B′) in WT 2–5-d-old OreR fed with 5% sucrose control solution during 24 h (white circle and yellow arrow show pH3-positive cell; inset B1). (C) Same as B, but flies were fed with 5% sucrose and 0.2 mg/ml colchicine. Note the increase in pH3-positive cells (compare C′ with B′). (D) Kinetochore marker Spc105 is detected in SAC-arrested ISCs (pH3 positive; yellow arrows). (E and F) mad2 or bubR1 reporter lines show GFP signal in SAC-arrested cells (yellow arrows). (G–J) 2–5-d-old mad2 or mps1 mutants flies fed with the same feeding method as described for WT flies in B and C. (K–P) Mitotic cells labeled with pH3 in intestines from control and flies where indicated RNAi was expressed. Flies were kept at 18°C during development to suppress the GAL4-UAS system and then were shifted to 29°C at eclosion day. After 48 h at 29°C on regular food, flies were shifted to vials with either sucrose or sucrose + colchicine solutions for 24 h. White circles and yellow arrows show pH3-positive cells. Bars: 40 µm (B, C, and G–P); 20 µm (B1 and G1); 10 µm (D–F). (Q) Number of mitotic cells present in first two fields of view of the posterior midgut after the pyloric ring (40× objective) in control, mad2RNAi, and mps1RNAi. Sucrose or colchicine feeding was initiated after flies spent 2 d at 29°C (0 h time point). n > 16 for all genotypes/conditions. ND, not determined; ****, P < 0.0001; Mann–Whitney U test.