Figure 1.
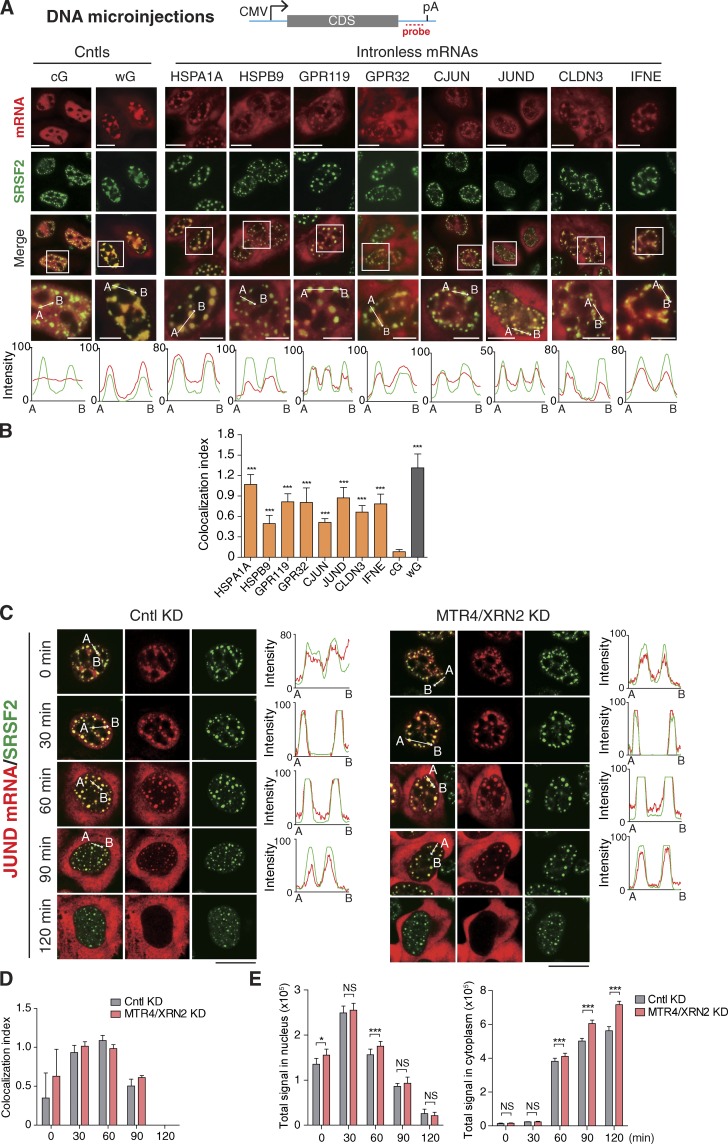
Exogenously expressed naturally intronless mRNAs associate with NSs. (A) Top: Schematic of reporter constructs. Sequences from the vector and the genes of interest are indicated as a cyan line and gray bar, respectively. The positions of the promoter, polyA (pA) site, and FISH probe are indicated. Bottom: Equal amounts of reporter constructs were microinjected into HeLa nuclei, and α-amanitin (4 µg/ml) was added 20 min after injection. At 30 min (cG and wG), 1 h (CJUN and JUND), 2 h (HSPA1A), or 4 h (others) after the addition of α-amanitin, FISH with the 3′ vector probe and IF with the SRSF2 antibody were performed. Higher magnification of the boxed regions is shown. The red and green lines in the graphs show the intensity of the FISH and SRSF2 IF signal along the freely positioned arrow indicated from A to B, respectively. CMV, cytomegalovirus; CDS, coding sequence. (B) Colocalization index of mRNA foci with SRSF2 speckles in each group shown in A. (C–E) Confocal microscopic images showing the JUND mRNA transcribed from the microinjected reporter construct and SRSF2 in HeLa cells treated with Cntl or MRT4/XRN2 siRNA for 72 h. The red and green lines in the graphs show the intensity of the FISH and SRSF2 IF signal, respectively (C). Colocalization indexes of the JUND FISH foci and SRSF2 dots at each time point are shown in D. Quantifications of nuclear and cytoplasmic JUND mRNA FISH signals are shown in E. Data represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments; n = 10. Bars: 10 µm (magnification); 20 µm (others). Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired t test. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.01. KD, knockdown.