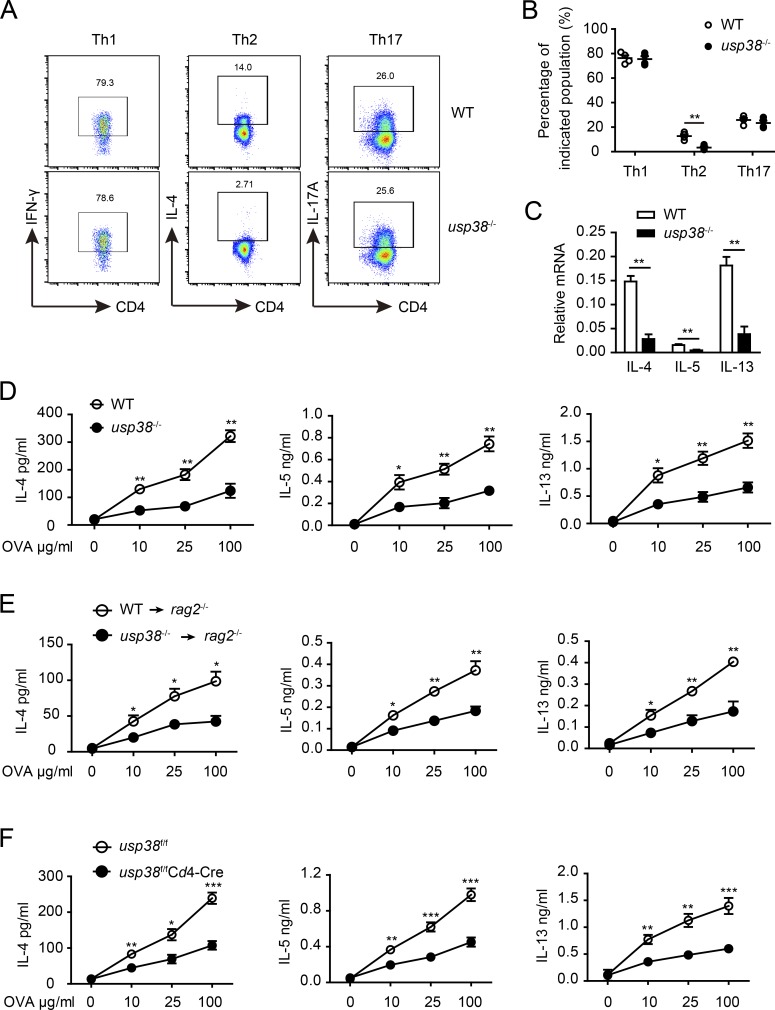
Figure 7.
USP38 is required for Th2 differentiation both in vitro and in vivo. (A) Flow chart of the indicated helper T cell subpopulations from cultures of usp38−/− or WT naive CD4+ T cells that were differentiated under Th1-, Th2-, or Th17-skewing conditions for 5 d. (B) Percentages of T cell subsets as shown in A. (C) mRNA levels of Il4, Il5, and Il13 in the Th2 cells obtained from A. (D) Concentrations of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 determined by ELISA in the supernatants from 3 d OVA-stimulated splenocytes out of WT or usp38−/− mice that were immunized with OVA in alum intraperitoneally for 7 d. (E) Concentrations of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 determined by ELISA in the supernatants from 3-d OVA-stimulated splenocytes out of the rag2−/− recipient mice that were transferred with WT or usp38−/− CD4+ T cells mixed with WT B cells at ratio of 1:1 and were immunized the next day with OVA in alum for 7 d. (F) Concentrations of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 determined by ELISA in the supernatants from 3-d OVA-stimulated splenocytes out of usp38f/fCd4-Cre and littermate control mice (usp38f/f) that were immunized as D. Data are representative of four (A–C), three (D and F), or two (E) independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t test; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Error bars indicate the mean ± SEM.