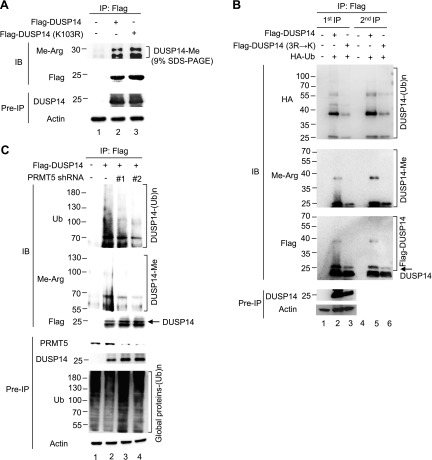
Figure 4.
DUSP14 methylation is essential for its ubiquitination. A) Methylation of DUSP14 ubiquitination-defective mutant (K103R) was comparable to that of wild-type DUSP14. Flag-DUSP14 wild-type or ubiquitination-defective mutant (K103R) was transfected into HEK293T cells. Flag-tagged DUSP14 proteins were immunoprecipitated from transfected cells with anti-Flag antibody and then immunoblotted with anti–methyl-arginine antibody. Methylated DUSP14 proteins were fractionated on 9% SDS-PAGE. B) DUSP14 methylation regulated its ubiquitination. Flag-DUSP14 wild-type or mutant (3R→K) was cotransfected with HA-ubiquitin into HEK293T cells. Flag-tagged DUSP14 was immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody (first IP); half of the first anti-Flag immunoprecipitates were denatured, followed by a second round of immunoprecipitation (second IP) with anti-Flag antibody. Immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with anti-HA, anti–methyl-arginine, or anti-Flag antibody. The protein markers used in this figure were different from those in A and C. Methylated DUSP14 proteins were fractionated on 9% SDS-PAGE. C) DUSP14 methylation was reduced by PRMT5 shRNA knockdown. Flag-DUSP14 were cotransfected with PRMT5 shRNA #1 or #2 into HEK293T cells. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody and then immunoblotted with anti-ubiquitin (Ub), anti–methyl-arginine, or anti-Flag antibody. The cell lysates were also directly immunoblotted with anti-ubiquitin antibody to detect global ubiquitination in cells. Methylated DUSP14 proteins were fractionated on 6% SDS-PAGE; the <50 kDa methyl-arginine bands were run off the gel. Arrowhead indicates the DUSP14 protein (upper band of the doublet). Data shown are representatives of 3 independent experiments.