Figure 1.
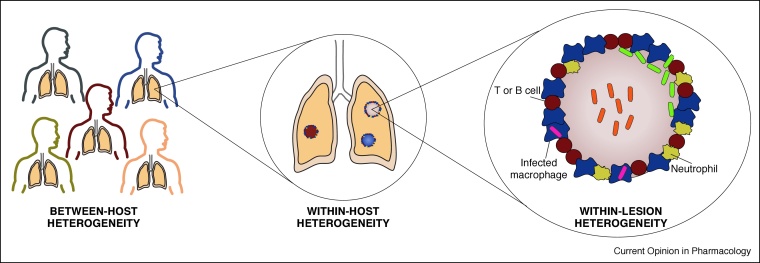
Heterogeneity in TB disease impacts the response to treatment. Heterogeneity is evident at multiple levels in TB disease [29••,48,49]. Differences in host genetics, immune status, co-infections and socioeconomic factors can impact susceptibility to TB infection and progression of disease. Once an individual becomes infected with Mtb and develops TB disease, the immune response and the response to TB chemotherapy can vary between TB lesions leading to differences in the kinetics of resolution between lesions, depicted here by different coloured lesions in the lung, and may result in the development of drug resistance in subpopulations of Mtb within distinct lesions [30].Within granulomas, spatial heterogeneity can result in drug gradients and metabolic changes in Mtb populations which differentially affect drug efficacy [50] and may result in phenotypic heterogeneity among populations of bacilli within a granuloma.