Figure 2. EcI Is a Conserved Membrane Transporter That Is Expressed Ubiquitously during Development.
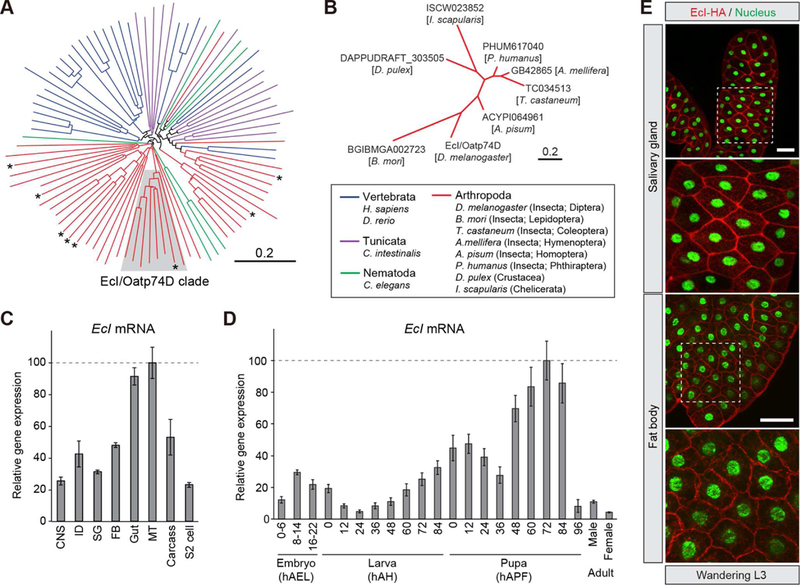
(A, B) EcI/Oatp74D has orthologs in a broad range of insects and other arthropods that utilize ecdysteroids as the molting hormone. (A) Neighbor-joining unrooted phylogenetic tree constructed using entire amino acid sequences of 8 Drosophila melanogaster Oatps (asterisks) and 82 other OATP proteins from vertebrates, a tunicate, arthropods, and a nematode. Protein names and GenBank accession numbers are listed in Table S2. Shaded area indicates the clade containing EcI/Oatp74D. (B) Neighbor-joining unrooted phylogenetic tree constructed using entire amino acid sequences of EcI/Oatp74D clade proteins that are shaded in (A). Scale bars indicate an evolutionary distance of 0.2 amino acid substitutions per position.
(C, D) EcI is expressed ubiquitously during development. (C) Relative expression levels of EcI/Oatp74D in various tissues and S2 cells, as assessed by qRT-PCR. Tissues were dissected from wandering third instar larvae (w1118). CNS, central nervous system; ID, imaginal disc; SG, salivary gland; FB, fat body; MT, Malpighian tubule. (D) Developmental changes in the relative expression level of EcI in the whole body, as assessed by qRT-PCR. Samples were collected from w1118 animals. hAEL, hours after egg laying; hAH, hours after hatching; hAPF, hours after puparium formation. Adult cDNA samples were prepared from flies at 24 hours after eclosion. Values are shown as percentages relative to the maximum level. All values are the means ± SD (n = 3).
(E) HA-tagged EcI is localized at the plasma membrane. fkh-Gal4 or Cg-Gal4 > UAS-EcI-HA wandering third instar larvae were immunostained for HA (red) and nuclei (green). Scale bars, 100 µm.
