Figure 5. EcI Cell-Autonomously Regulates Ecdysone Signaling and Facilitates Cellular Uptake of Ecdysteroids in Vivo.
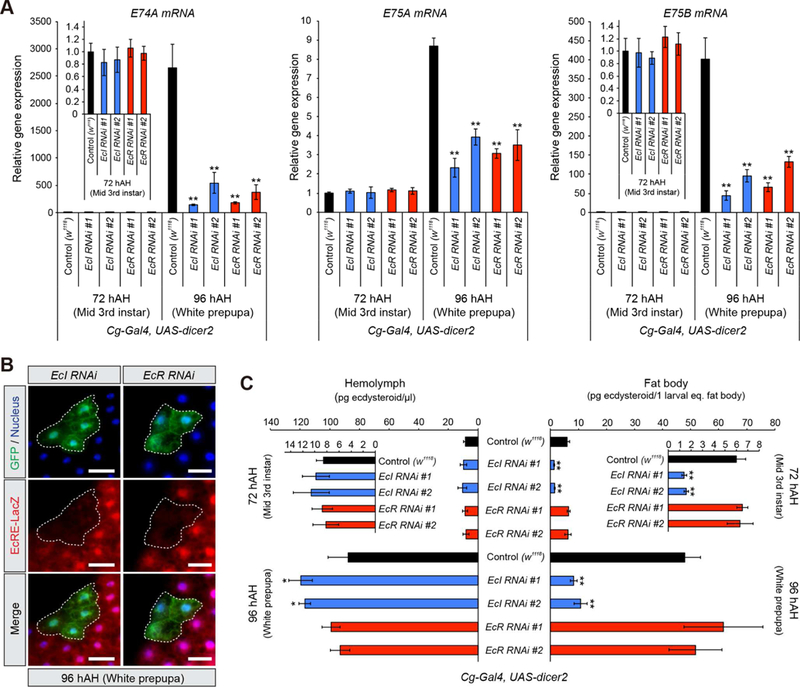
(A) Relative expression levels of ecdysone-inducible genes (E74A, E75A and E75B) in the fat body at 72 and 96 hAH, as assessed by qRT-PCR. Two independent UAS-RNAi lines for EcI and EcR were used. Cg-Gal4 > UAS-dicer2 was used as a fat body-specific Gal4 driver. Values were calculated relative to the expression level of each gene at 72 hAH in control.
(B) Cell-autonomous requirement of EcI and EcR for ecdysone signaling in the fat body. Clones of fat body cells expressing EcI-RNAi #1 or EcR-RNAi #1 with dicer2 were labeled with GFP. EcRE-LacZ reporter gene was used to monitor the activity of ecdysone signaling. hs-flp;; Act>CD2>GAL4, UAS-nlsGFP was used to generate GFP-marked flip-out clones. Flippase activity was induced by 10 min heat shock. The fat body from white prepupae at 96 hAH was immunostained for LacZ (red), GFP (green) and nuclei (blue). Scale bars, 50µm.
(C) Quantification of ecdysteroids in the hemolymph and fat body at 72 and 96 hAH, as assessed by ELISA. UAS-RNAi and Gal4 lines used were the same as in (A).
All values are the means ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 from Student’s t test compared to control.
