Figure 7. HJURP copurifies with the MCM2–7 helicase complex and simultaneously interact with MCM2-CENP-A/H4 proteins.
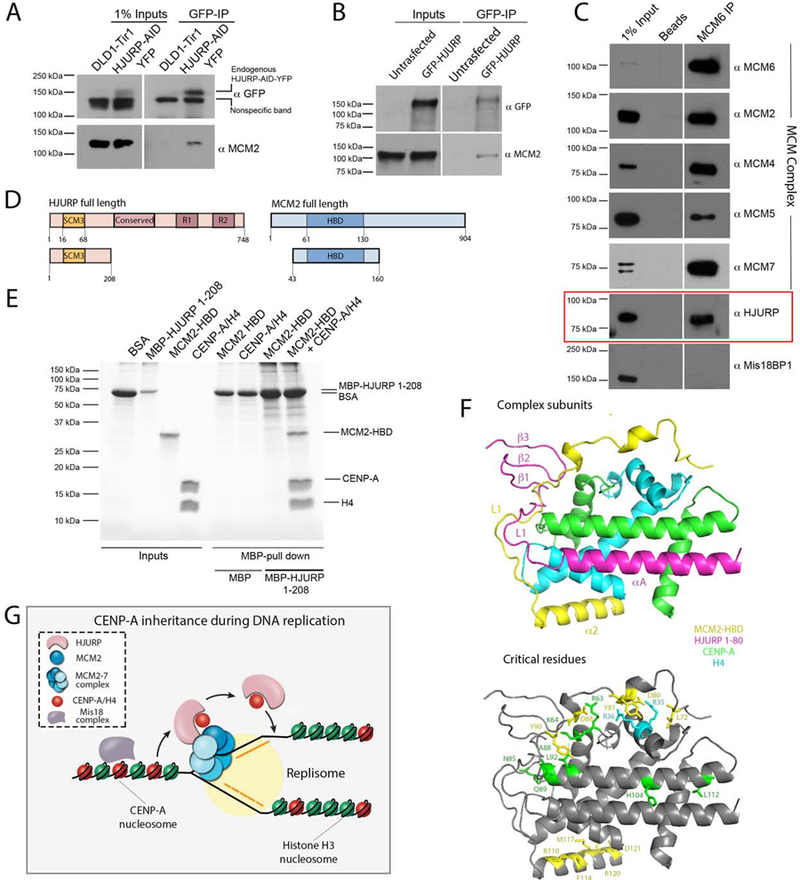
(A) Immunoblot analysis of GFP immunoprecipitation (IP) demonstrating the interaction of endogenous HJURP with endogenous MCM2. HJURP-AID-YFP DLD-1 cells were used as an input for the IP and samples were analyzed with indicated antibodies. (B) Immunoblot analysis of GFP IP performed from HEK293 cells overexpressing HJURP-GFP. Samples were analyzed with indicated antibodies. The blots in (A) and (B) were separated in two sections as the input and IP fractions correspond to different exposure times. (C) Immunoblot analysis of MCM6 IP performed from HEK293-derived cell lysates treated with Micrococcal nuclease. Samples were analyzed with indicated antibodies. (D) Schematic representation of constructs used in E. (E) Coomassie gel of MBP-HJURP1−208 in vitro pull down demonstrating the interaction with MCM2-HBD only in the presence of CENP-A/H4 heterodimer. (F) The superimposed model of 3R45 and 5BNX crystal structures where H3.3 and CENP-A were used as a reference. MCM2-HBD is shown in yellow, HJURP1−80, CENP-A and H4 are shown in pink, green, and aqua, respectively. Residues critical for facilitating the interaction of MCM2 with histones and mediating CENP-A recognition by HJURP are depicted in bottom panel. (G) The model of inheritance of CENP-A nucleosomes across DNA replication. MCM2–7 helicase complex is involved in unwinding chromatin ahead of the replication fork. HJURP is associated with MCM2–7 complex, and both MCM2 and HJURP can bind CENP-A nucleosomes simultaneously. The ability of CENP-A to be recognized by HJURP through the CATD domain and MCM2 through the R63-K64 motif are both essential for facilitating CENP-A retention across S phase and maintaining centromere identity.
