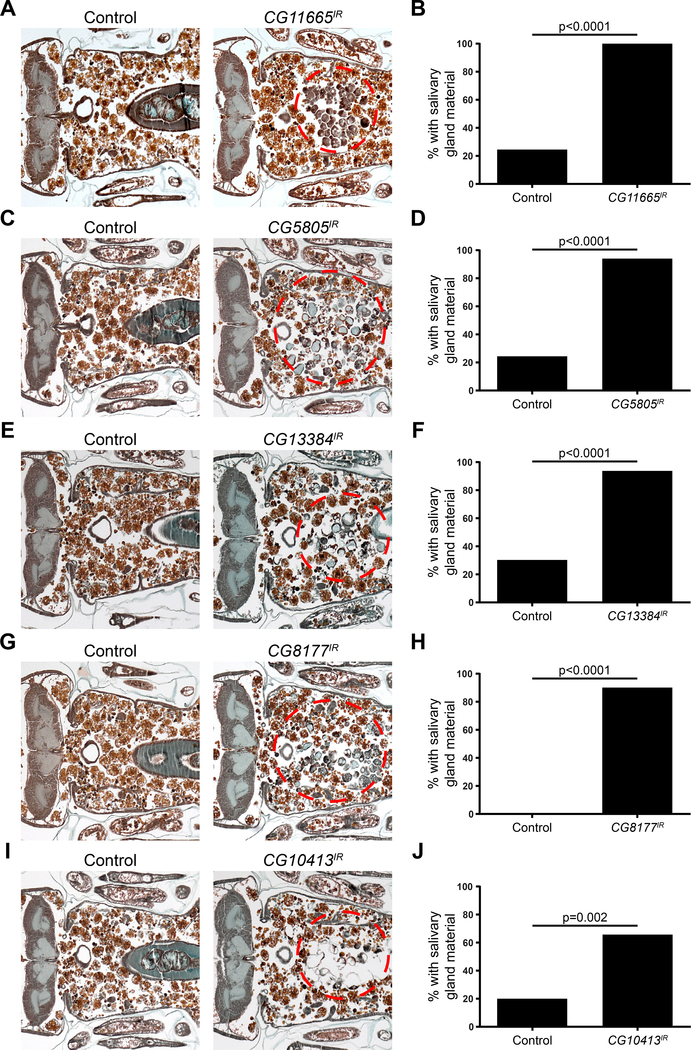
Figure 1. SLC genes that are required for salivary gland cell death.
(A) Samples from control animals (w/+; +; UAS-CG11665IR/+), n= 16 (left), and those with salivary gland-specific knockdown of CG11665 (fkh-GAL4/w; +; UAS-CG11665IR/+), n = 18 (right), analyzed with histology for the presence of salivary gland material (red dotted circle) 24h after puparium formation. (B) Quantification of data from (A). (C) Samples from control animals (w/+; +; UAS-CG5805IR/+), n= 20 (left), and those with salivary gland-specific knockdown of CG5805 (fkh-GAL4/w; +; UAS-CG5805IR/+), n = 24 (right), analyzed with histology for the presence of salivary gland material (red dotted circle) 24h after puparium formation. (D) Quantification of data from (C). (E) Samples from control animals (w/+; +; UAS-CG13384IR/+), n= 20 (left), and those with salivary gland-specific knockdown of CG13384 (fkh-GAL4/w; +; UAS-CG13384IR/+), n = 20 (right), analyzed with histology for the presence of salivary gland material (red dotted circle) 24h after puparium formation. (F) Quantification of data from (E). (G) Samples from control animals (w/+; UAS-CG8177IR/+; +), n= 20 (left), and those with salivary gland-specific knockdown of CG8177 (fkh-GAL4/w; UAS-CG8177IR/+; +), n = 23 (right), analyzed with histology for the presence of salivary gland material (red dotted circle) 24h after puparium formation. (H) Quantification of data from (G). (I) Samples from control animals (w/+; UAS-CG10413IR/+; +), n= 20 (left), and those with salivary gland-specific knockdown of CG10413 (fkh-GAL4/w; UAS-CG10413IR/+; +), n = 24 (right), analyzed with histology for the presence of salivary gland material (red dotted circle) 24h after puparium formation. (J) Quantification of data from (I). See also Figure S1.