Figure 6.
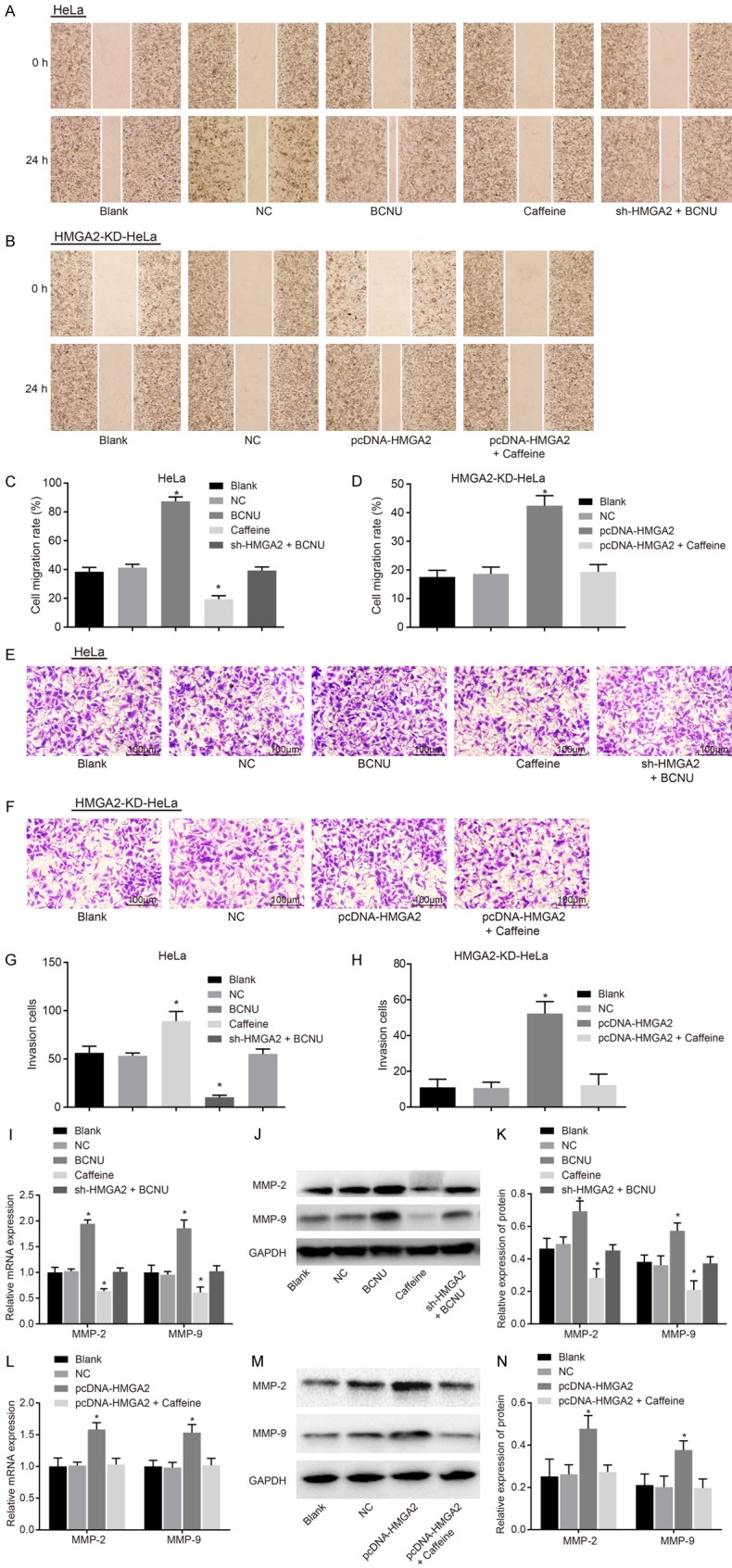
HMGA2 silencing or inhibition of the ATR/Chk1 signaling pathway inhibited migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells. Notes: In the HeLa cell line, the scratch test (A) and migration rate (C) indicated that caffeine reduced cervical cancer cell migration ability; moreover, Transwell assay (E) and number of invasion cells (G) demonstrated reduced cervical cancer cell invasion in response to caffeine; RT-qPCR (I) and western blot analysis (J, K) suggested that expression of metastasis-related genes (MMP-2, MMP-9) was decreased; In the HMGA2-KD-HeLacell line, the scratch test (B) and migration rate (D) indicated that pcDNA-HMGA2 promoted cervical cancer cell migration ability; moreover, Transwell assay (F) and number of invasion cells (H) demonstrated increased cervical cancer cell invasion; RT-qPCR (L) and western blot analysis (M, N) suggested that expression of metastasis-related genes (MMP-2, MMP-9) was increased; *, P<0.05 vs. the blank group; the migration distance is measurement data, expressed by mean ± standard deviation; the number of cell invasion is enumeration data; comparison in the migration distance and invasion ability was performed by one-way ANOVA; the experiment was repeated 3 times.
