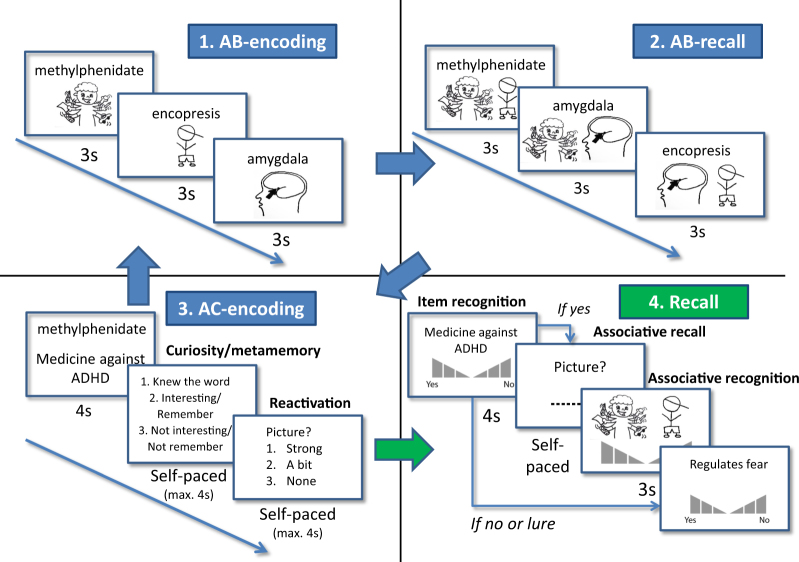
Fig. 1.
Experimental design. During encoding (blue panels), participants learned 8 ABC-combinations during 10 (experiment 1) or 8 blocks (experiment 2) in three phases: AB-encoding, AB-recall and AC-encoding. In experiment 1, participants were asked whether they thought what they learned was interesting (curiosity), and in experiment 2 they were asked whether they thought they would remember the association (metamemory). In both experiments, they were subsequently asked how strongly they reactivated the associated picture (reactivation). After all blocks were encoded (steps 1–3) and a short math task was performed (not depicted), participants performed a recall task (step 4; green panel) including item recognition (do you recognize this description?), associative recall (given the description, write down the associated picture), and associative recognition (given the description, pick the associated picture) tests respectively. Item recognition and associative recognition tasks also included confidence levels. See for more specific details regarding the design and stimuli the sections “Stimuli” and “Procedure”