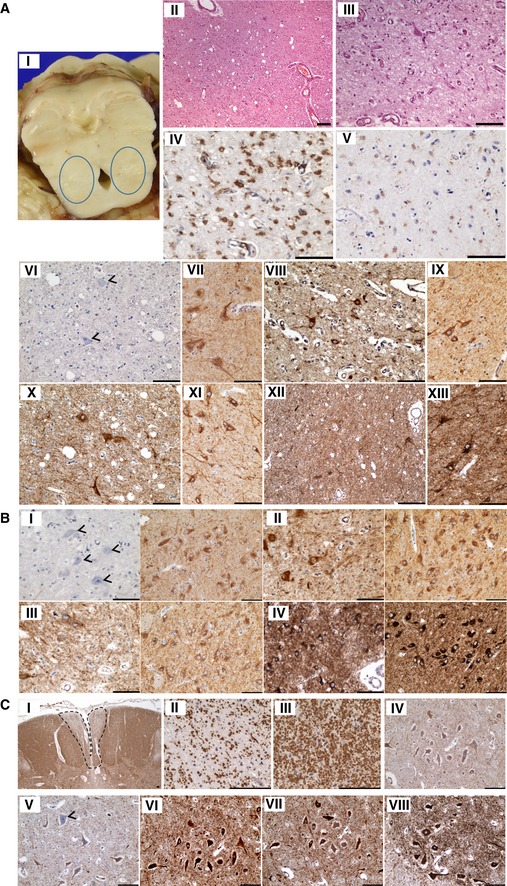
Figure EV2. Neuropathology: Bilateral cavitation of the pons, demyelination of the fasciculus gracile tract and downregulation of complex I subunits NDUFS3 and NDUFB8.
-
AThe pons demonstrate bilateral cavitation (i and ii), specifically affecting the pedunculopontine nucleus, accompanied by microvascular proliferation (iii), reactive astrogliosis (iv) and microglial activation (v). There is downregulation of NDUFS3 (vi; arrowheads) expression within neurons and the surrounding neuropil (control staining: vii), while SDHA (viii; control shown in ix), COXI (x; control shown in xi) and ATP5B (xii; control shown in xiii) expression is maintained within normal levels.
-
BThe neurons of the substantia nigra also reveal a loss of NDUFS3 (i; arrowheads, control shown on right) expression, while SDHA (ii left panel; control shown on right), COXI (iii left panel; control shown on right) and ATP5B (iv left panel; control shown on right) expression levels are comparable to control.
-
CThe fasciculus gracile tracts reveal demyelination (i and ii), while the adjacent fasciculus cuneatus is myelinated (iii). Neuronal population density of the motor neurons is maintained, while there is a loss of NDUFB8 (iv) and NDUFS3 expression (v) and intact SDHA (vi), COXI (vii) and ATP5B (viii) expression.
