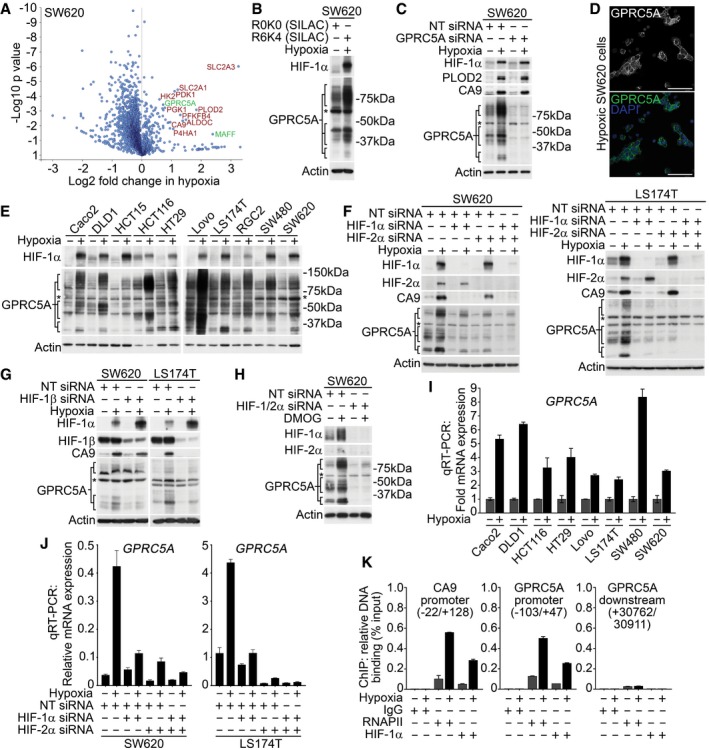
-
A
SILAC‐based proteomics data identify known (red) and novel (green) hypoxia‐induced proteins in SW620 cells. One‐sample t‐test was performed.
-
B
Western blotting confirmed GPRC5A as a hypoxia‐induced protein in SILAC lysates.
-
C
Validation of GPRC5A Western blot data using siRNA. *Non‐specific band of ˜60 kDa not depleted by GPRC5A siRNA.
-
D
Confocal microscopy showing plasma membrane GPRC5A expression in hypoxic SW620 cells (scale bars: 75 μm).
-
E
Western blotting showing GPRC5A upregulation by hypoxia in a panel of colorectal tumour cell lines.
-
F
Basal & hypoxia‐induced GPRC5A protein expression was decreased by HIF‐1/2α depletion.
-
G
Depletion of HIF‐1β decreased GPRC5A protein upregulation in hypoxia.
-
H
Hypoxia mimetic DMOG induced HIF‐1/2α, CA9 and GPRC5A protein expression. Dual HIF‐1/2α depletion reduced GPRC5A induction by DMOG.
-
I
qRT–PCR demonstrating that GPRC5A mRNA was upregulated by hypoxia (n = 3). GPRC5A was normalised to HPRT (error bars ± SD).
-
J
qRT–PCR demonstrating that HIF‐1/2α depletion decreased GPRC5A induction during hypoxia (n = 3). GPRC5A was normalised to HPRT (error bars ± SD).
-
K
ChIP‐PCR analyses identify HIF‐1α binding to the GPRC5A promoter region containing a putative optimal HRE (error bars ± SD, n = 3).
Data information: Asterisks (*) indicate non‐specific band. Level adjustments were made to images in Adobe Photoshop post‐acquisition for clarity (equal changes applied to the entire image). Representative examples of
= 3 independent experiments are shown.