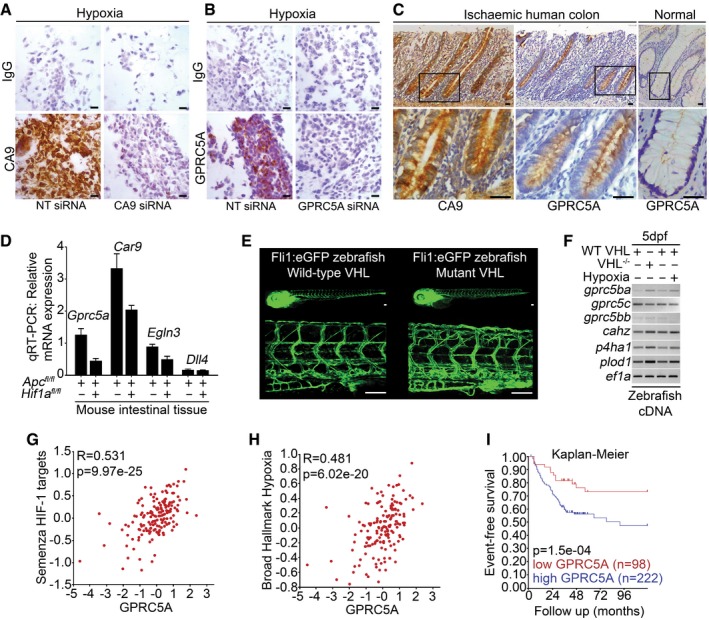
Figure 2. GPRC5A is hypoxia/HIF‐induced in vivo .
-
A, BExpression of CA9 and GPRC5A in formalin‐fixed paraffin‐embedded hypoxic SW620 cells by IHC. Reduced CA9 and GPRC5A expressions with siRNA confirm antibody specificity (scale bars: 200 μm).
-
CIHC analysis of serial sections from human colorectal tissue from patients with mesenteric ischaemia (strangulated colon). GPRC5A is co‐expressed with CA9 in the colonic epithelial cells (scale bars: 50 μm).
-
DQuantitative RT–PCR analysis of mouse intestinal tissue. Gene expression was normalised to housekeeping gene Tbp. Raw data from three independent experiments (n = 3 mice) are shown (error bars ± SEM).
-
ETg[fli1:eGFP; vhl −/−] and Tg[fli1:eGFP] zebrafish embryos (5 days post‐fertilisation) demonstrate excessive angiogenesis and increased expression of HIF target genes (scale bars: 100 μm).
-
Fgprc5ba was induced in vhl mutant zebrafish embryos and fli1:eGFP zebrafish embryos exposed to 5% O2 (vs. normoxia) for 24 h (RT–PCR).
-
G, HBioinformatic analysis of transcriptomics dataset GSE24551. Gene set analyses reveal GPRC5A mRNA strongly correlated with HIF/hypoxia gene signatures. GSEA datasets used were Semenza_HIF1_Targets (M12299) Broad_Hallmark_Hypoxia (M5891). Analysis was performed using R2 (http://r2.amc.nl).
-
IKaplan–Meier curve following analysis of transcriptomics dataset GSE24551. Event‐free survival is significantly reduced in patients with tumours expressing high levels of GPRC5A mRNA. Analysis was performed using R2 (http://r2.amc.nl).
