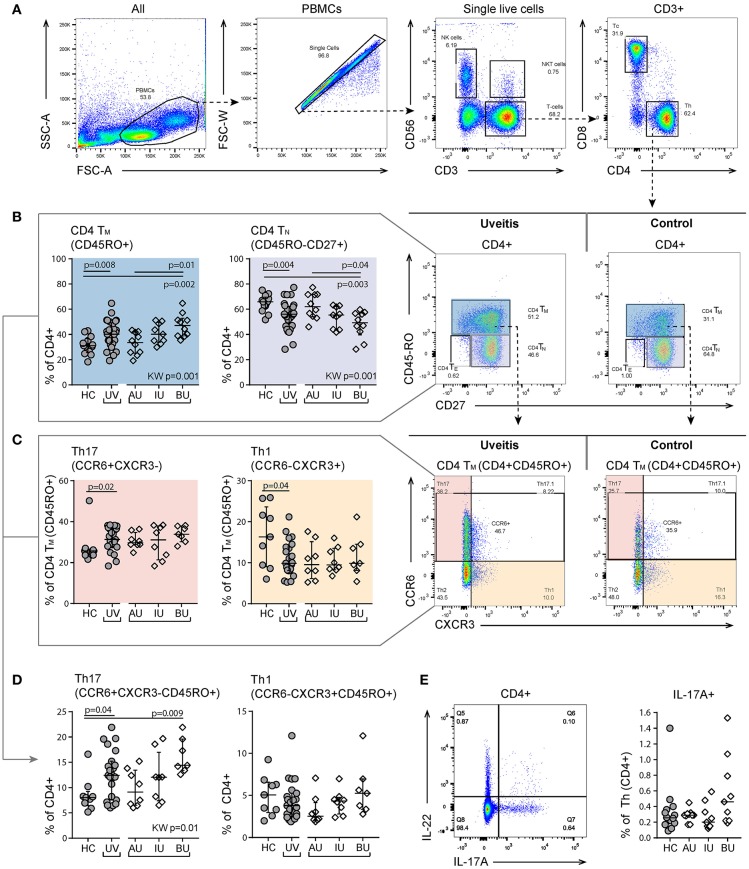
Figure 2.
Heterogeneity in memory T cell subsets and abundance of CXCR3-CCR6+ (Th17) cells between uveitis subtypes. (A) Gating strategy of a representative sample used to identify T helper (Th. CD3+CD4+) and cytotoxic T cells (Tc. CD3+CD8+). (B) Shift in proportion from naïve to memory T helper cells in uveitis patients compared to controls. The proportion of CD4+TN and CD4+TM cells shows heterogeneity between the uveitis subtypes and the observed difference between uveitis and healthy controls is mainly driven by BU patients. (C) Within the CD4+TM there is an increase of Th17 (CCR6+CXCR3-) and a decrease in Th1 (CCR6-CXCR3+) cells in uveitis patients compared to healthy controls. (D) BU displayed an increase in Th17 cells within the total CD4+ T cell population compared to the other patient groups. (E) left: gating strategy used to identify IL-17A expressing CD4+ T helper cells using the intracellular cytokine panel. Right: percentage of IL-17A+ cells within the total CD4+ T cell population. The gating of intracellular cytokines (including IL17A) from CD4 T cells in given in more detail in Figure S2. Bars indicate the median and interquartile range. P-values between HC and UV are from Wilcoxon rank-sum test, p-values between uveitis subgroups are from Kruskal–Wallis (KW) test with post-hoc Dunn's correction for multiple testing. AU, HLA-B27 associated anterior uveitis; BU, Birdshot uveitis; HC, healthy control; IL, interleukin; IU, idiopathic intermediate uveitis; TE, effector T cell (CD45RO-CD27-); Th, T helper cell (CD3+CD4+); TM, memory T cell (CD45RO+); TN, naïve T cell (CD45RO-CD27+); PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; UV, all uveitis patients combined.