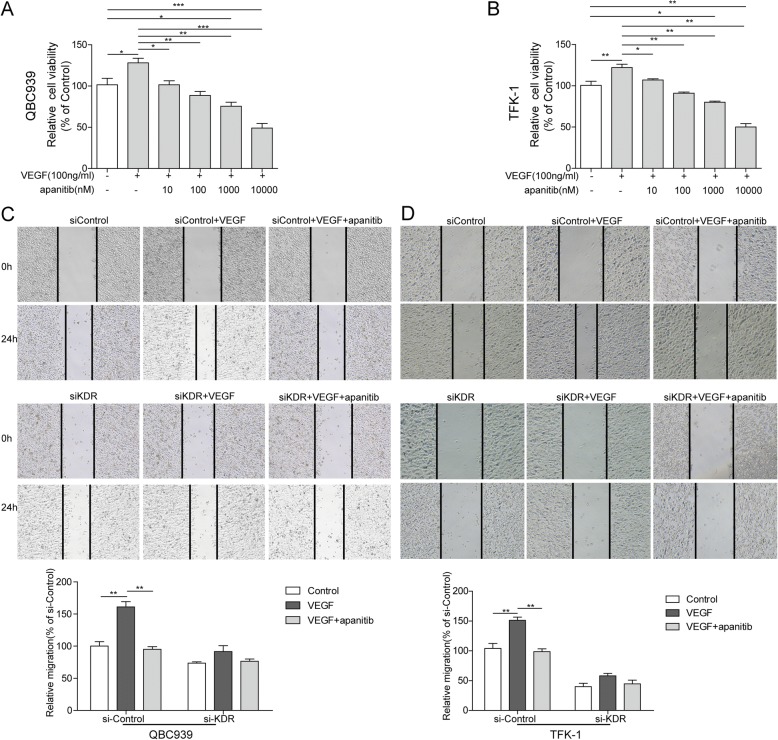
Fig. 4.
Apatinib inhibits VEGF- induced cell migration and invasion (a-b) Cell viability of QBC939 (A) and TFK-1 (b) cells. Cells were treated with 100 ng/ml rhVEGF for 2 h and then treated with 10, 100, 1,000 and 10,000 nM of apatinib for 24 h. 100 ng/ml rhVEGF significantly increased relative cell viability (compared with 0 ng/ml rhVEGF+ 0 nM apatinib group)and 10–100 nM of apatinib reverses this increase (compared with 100 ng/ml rhVEGF group). Furthermore, 1,000 and 10,000 nM of apatinib inhibite relative cell viability compared with 0 ng/ml rhVEGF+ 0 nM apatinib group. Data are representative of three independent experiments.*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01. c-d QBC939 (c) and TFK-1(d) cells migration was measured by wound-healing analysis for 0 and 24 h. si-Control and and si-KDR cells grown in six-well plates were scratched and treated with PBS, VEGF (100 ng/ml), or VEGF (100 ng/ml) combined with apatinib (100 nM) for 24 h. Data are representative of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01