Figure 3.
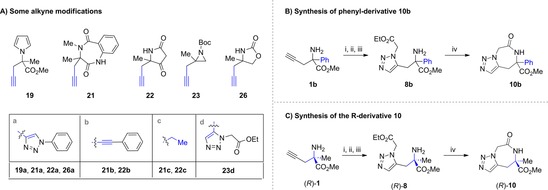
(A) Exemplification of the synthesis of other derivatives via alkyne modifications. Reaction conditions: 19 a, 21 a, 22 a, 26 a: azidobenzene, CuSO4⋅5 H2O, tBuOH:H2O, rt, 72–92 %; 21 b and 22 b: PdCl2(PPh3)2, CuI, Et3N, benzyl 2‐iodobenzoate, DMF, rt, 16 h, 60 % and 26 %, respectively; 21 c and 22 c: Pd/C, H2, MeOH, rt, 2 h, 69 % and 87 %, respectively; 23 d: ethyl 2‐azidoacetate, Cp*RuCl(COD), PhMe, rt −60 °C, 21 h, 42 % (B) Synthesis of the phenyl‐containing derivative. Reaction conditions: i) Boc2O, THF, 70 °C, o/n, 84 %; ii) ethyl 2‐azidoacetate, Cp*RuCl(COD), PhMe, 80 °C, 1 h, 87 %; iii) TFA, CH2Cl2, 2 h then NaHCO3, (quantitative yield); iv) PhMe, 150 °C, o/n, 76 %. (C) Synthesis of an enantiopure component of the library. Reaction conditions: i) Boc2O, THF, 70 °C, o/n, 90 %; ii) ethyl 2‐azidoacetate, Cp*RuCl(COD), PhMe, 50 °C, 1 h, 76 %; iii) TFA, CH2Cl2, 2 h then NaHCO3, 93 %; iv) PhMe, 150 °C, o/n, 79 %.
