Figure 1.
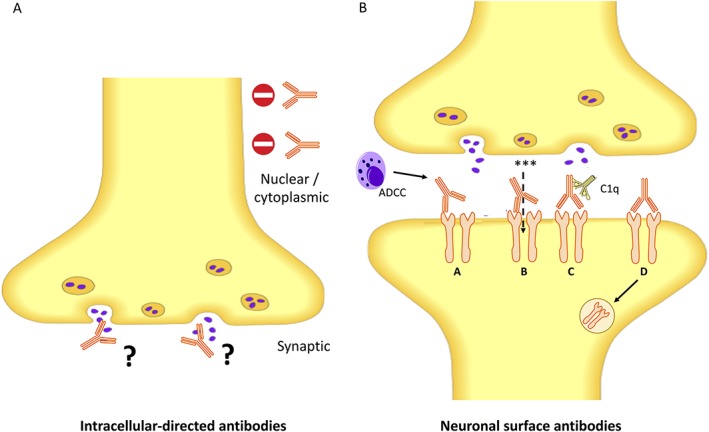
Autoantibodies directed at intracellular and extracellular domains of neuronal proteins. (A) Autoantibodies against constitutive nuclear or cytoplasmic proteins do not appear to gain access to their targets, whereas those directed against predominantly intracellular synaptic proteins may gain access at the time of vesicle fusion. (B) Pathogenic mechanisms of neuronal surface proteins. Neuronal surface proteins have a direct pathogenic effect on the antigen through various mechanisms: (A) antibody‐dependent cell‐mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), (B) direct target modulation through agonist/antagonist effects, (C) complement activation, and (D) antigen internalization. * = ions; red circle with horizontal white line denotes a “no entry” sign; C1q, complement component 1q.
