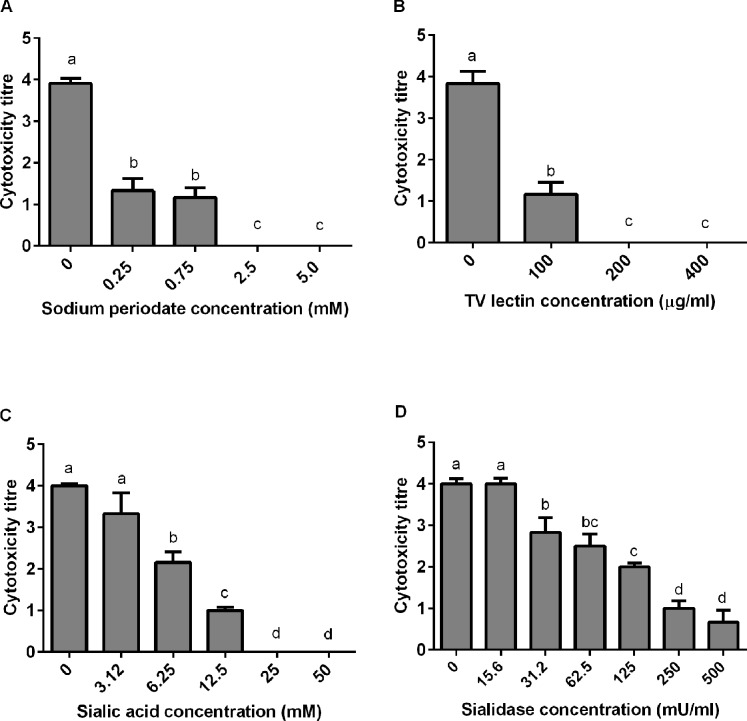
Fig 5.
A-D. Effect of sodium periodate, lectin, sialic acid and sialidase treatment on NetF binding molecules present on the surface of EO cells. A) Cytotoxicity of NetF on EO cells pretreated with sodium periodate. Cells were incubated with various amounts of sodium periodate at 37°C for 20 min in order to destroy surface carbohydrates with vicinal OH groups. The cells were then washed and incubated with rNetF for 4 h before evaluating the toxicity score. B) Inhibition of NetF cytotoxicity to EO cell surface by TV lectin treatment. The EO cells were incubated with different concentrations of Triticum vulgaris lectin at 37°C for 20 min. The cells were then washed and incubated with rNetF for 4 h before evaluating the toxicity score. C) Inhibition of NetF cytotoxicity to EO cell by free sialic acid. rNetF was mixed with various amounts N-acetyl neuraminic acid (sialic acid) and incubated for 20 min at 37°C. This mixture was then transferred on EO cells and incubated for 4 h before evaluating the toxicity score. D) Effect of sialidase treatment on toxicity of NetF to EO cells. The EO cells were treated with different amounts of sialidase purified from Arthrobacter ureafaciens for 1 h at 37°C. The cells were then washed and incubated with rNetF toxin for 4 h before evaluating toxicity score. The values are averages of triplicate assays in three experiments, with error bars representing standard deviation. Bars which are marked by the same letter did not differ significantly (P > 0.05).