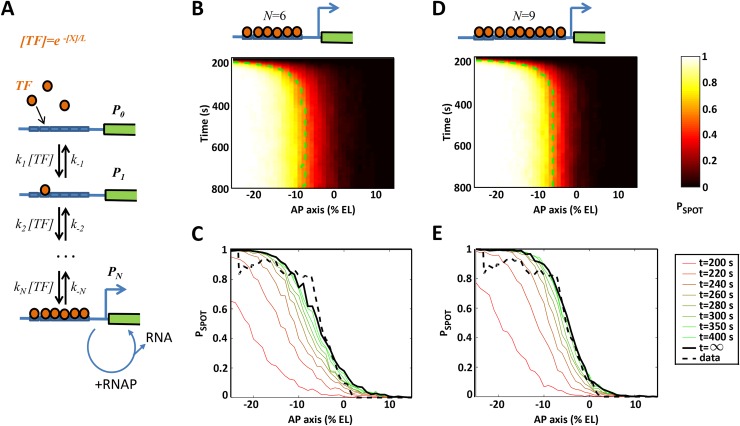
Fig 8. Modeling transcriptional regulation by the Bicoid transcription factor through interactions with the hb promoter operator sites.
A) A model of regulation by Bicoid transcription factor (TF) binding to multiple binding sites on the hb promoter coupled with stochastic transcription initiation. Transcription initiation is allowed only when the binding sites are fully bound. During this window, RNAP can randomly bind to the promoter and initiate transcription to produce mRNA. B or D) The model prediction for the probability of an active transcription locus (PSPOT(t), colorbar) as a function of time in the nuclear cycle and position along the AP axis for a model with 6 (B) or 9 (D) Bicoid binding sites. C or E) The simulated pattern evolution of PSPOT(t) along the AP axis over time (colored line), shown with the pattern predicted at steady state (solid black line) and the stable pattern extracted from the data in nc13 (dashed black line, as in Fig 7F). Panels C and E represent cuts in time of panels B and D, respectively. The kinetic parameters were chosen so as to match the observed hb pattern steepness and formation time at the boundary (PSPOT(t) = 0.5) (see S2 Table). The value of PSPOT(t) is calculated from 200 trajectories per AP position.