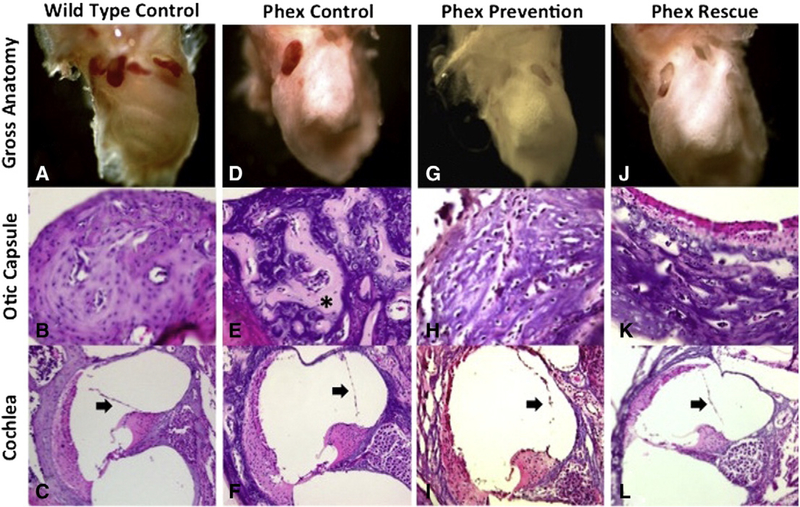
Fig. 2 –
Otic capsule and cochleamorphology. Wild-type control specimens (A–C) demonstrate normal mineralization and morphology of the otic capsule and cochlea. There is no distension of Reissner’smembrane (arrow). Phex control specimens (D–F) demonstrate dysmorphic grossmorphology and poor otic capsule mineralization with thick osteoid strands (*). Reissner’smembrane is distended, which is consistent with endolymphatic hydrops (arrow). The Phex prevention (G–I) and Phex rescue (J–L) groups still demonstrate altered grossmorphology and distention of Reissner’smembrane (arrow). Compared to the Phex control group, the two treatment arms show improved otic capsule mineralization with less osteoid deposition. Gross anatomy images were taken with low magnification on a stereomicroscope. The otic capsule and cochlea images were taken with a light microscope at 100× and 10× magnification, respectively.