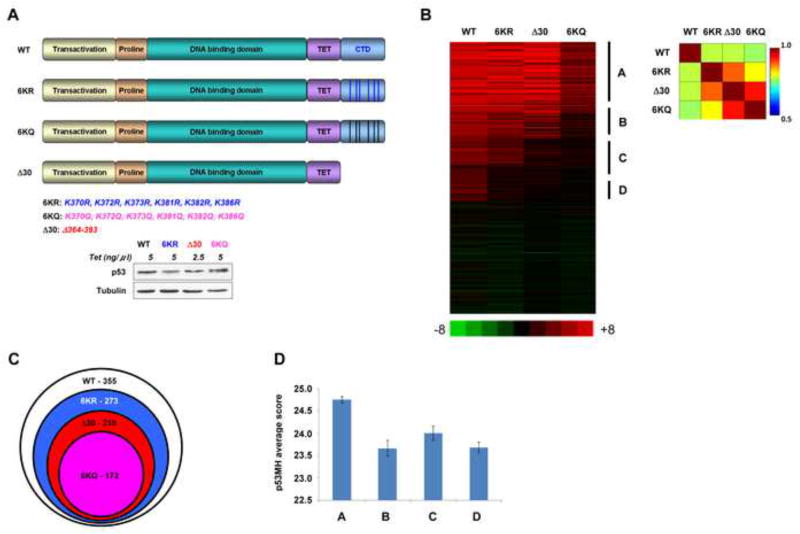
Figure 1. The p53 CTD is Required for Binding to Targets that Deviate from the Consensus Binding Sequence.
(A). Schematic representation of p53 CTD variants expressed in H1299 cells. The positions of C-terminal lysines mutated to either arginine or glutamine are indicated below. Relative expression levels of p53 proteins used in the ChIP-on chip experiment are shown below. (B). Heat-map representation of ChIP-on-chip results. The vertical lines indicate the clustering of four groups of p53 target sites that were bound by the proteins indicated above each group. Indicated on the right of the heat map are group A, representing the sites bound by all p53 forms; B representing the sites bound by all p53 proteins other than the 6KQ; C representing the sites bound by WT and 6KR p53 variants; D representing the sites bound exclusively by WT p53. On the right is the correlation matrix corresponding to the heat map. (C). Venn diagram showing the total number of sites bound by each p53 variant and their relationship. (D). Average and standard error of p53 binding site scores (calculated by p53MH algorithm) for each distinct group. Group A score is significantly different from those of the other groups (P<0.006, 0.04 and 0.0002; two sides Student T test for groups B, C and D, respectively). See also Figure S1.