Fig. 3. Ponatinib inhibits CCM lesion formation and progression in the CCM1-deficient CCM model.
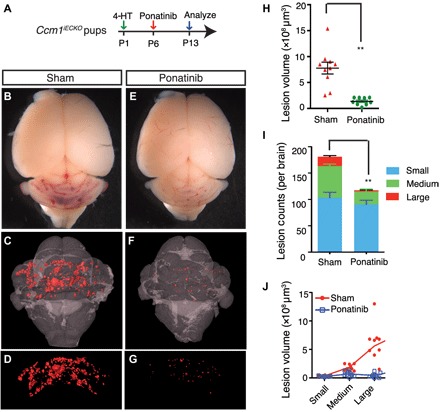
(A) Schematic of experimental design. Neonatal pups at P1 were induced with 4-HT and treated with ponatinib at P6. Brains were collected at P13 for micro–computed tomography (CT) analysis. (B to G) Micro-CT imaging of CCM lesions in Ccm1iECKO with (E to G) or without (B to D) ponatinib treatment. (H to J) Quantification of micro-CT analysis shows that ponatinib treatment in the Ccm1iECKO reduced CCM lesion burden by 72% (H) and total lesions number by 35% (I) compared with that of sham-treated controls. CCM lesions distribution analysis showing decreased number (I) and total volume (J) of medium and large lesions in ponatinib-treated Ccm1iECKO mice, but the number and collective volume of small lesions did not change. Error bars are shown as SEM, and significance was determined by Student’s t test. “**” indicates P < 0.001. n = 10 for the sham group, n = 9 for the ponatinib treatment group.
