Fig. 6. Ponatinib normalized MEKK3-induced signaling and endothelium ultrastructure in CCM mouse models.
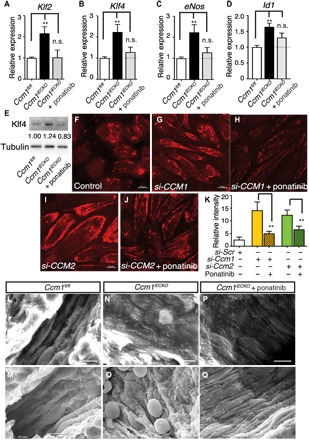
(A to D) Gene expression analysis of ponatinib-treated Ccm1iECKO mice. Ponatinib treatment at P6 normalized the increased expression of Klf2, Klf4, eNos, and Id1 in the freshly isolated brain endothelial cells from Ccm1iECKO mice as analyzed at P8. Error bars are shown as SEM, and significance was determined by one-way ANOVA, n = 6. “**” indicates P < 0.001; (E) Western blotting analysis of Klf4 protein level in freshly isolated brain endothelial cells. Band density ratios are shown underneath the Klf4 blot. (F to J) Immunocytochemistry analysis shows increased pMLC2 level in the si-CCM1 (G) and si-CCM2 (I) endothelial cells compared with control (F), while treatment with ponatinib returned pMLC2 levels to near baseline (H and J). (K) Quantification of pML2 relative fluorescence intensity. (L to Q) Scanning electron microscope images of murine brain microvessels in P30 mouse brains. In microvessels without CCM lesions (L and M), endothelium ridges are present and aligned in the direction of blood flow. In CCM lesions (N and O), endothelium is flattened and disorganized. CCM lesions treated with ponatinib (P and Q) show partially normalized ridge structures of endothelium and alignment in the direction of blood flow. Results are representative of three independent experiments.
