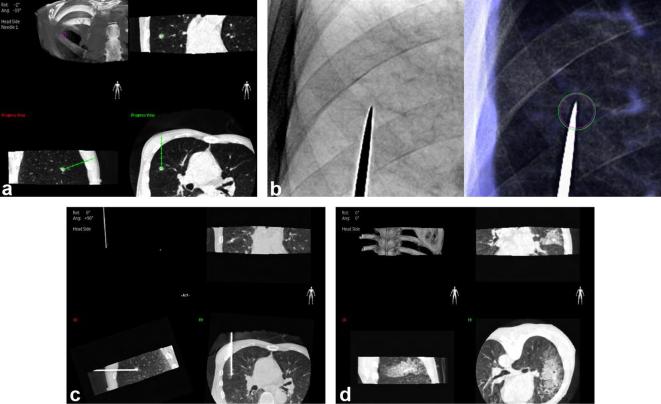
Figure 2. .
An example of CBCT virtual navigation-guided PTNB using virtual guidance software. Based on the preprocedural CBCT images, the operator determined the safest virtual needle pathway, specifying the skin entry site and virtual location of the needle tip (a). The C-arm automatically rotated in the direction of the virtual needle pathway and that of the X-ray, providing a fluoroscopic needle guidance view (bull’s eye view, b). The actual location of the needle tip was confirmed by intraprocedural CBCT (c). After tissue acquisition and removal of the needle, a postprocedural CBCT scan was obtained to check for the occurrence of complications (d).