Fig. 1. Schematic representation and purification process for RtxA and proRtxA.
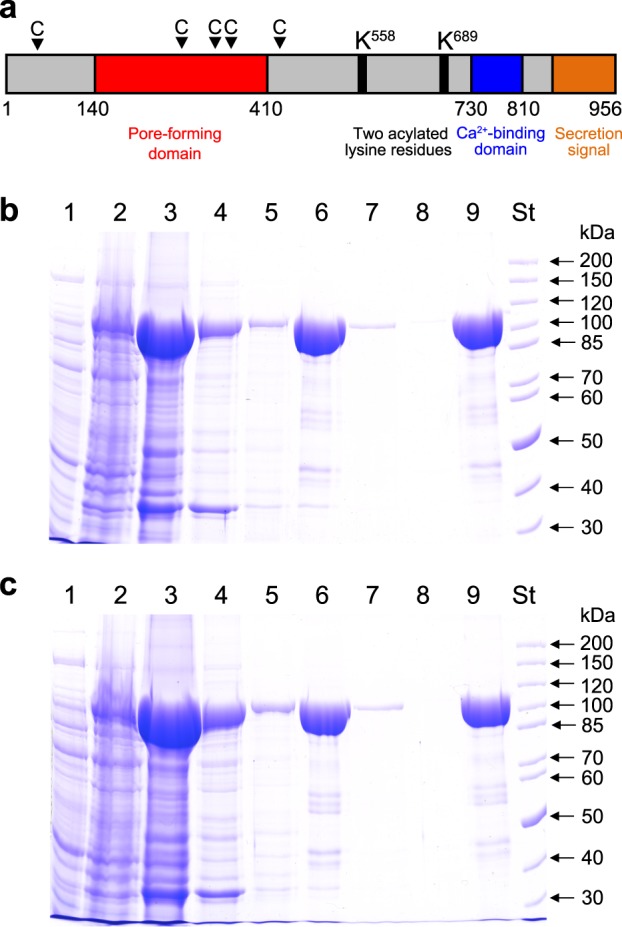
a Scheme of the K. kingae RtxA molecule, with several different areas predicted from homology with other RTX toxins. The arrowheads with a letter C indicate the predicted CRAC and CARC motifs. The RtxA (b) and proRtxA (c) proteins were produced in E. coli BL21/pMM100 cells and purified by a combination of affinity and hydrophobic chromatographies. Lanes: 1, crude extract from uninduced cells; 2, crude extract from cells induced with isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) to produce RtxA/proRtxA; 3, clarified crude urea extract from induced cells; 4, Ni-NTA agarose column flowthrough; 5, Ni-NTA agarose column wash; 6, fraction of eluted 105-kDa RtxA/proRtxA; 7, phenyl-sepharose column flowthrough; 8, phenyl-sepharose column wash; 9, fraction of eluted RtxA/proRtxA; and St, molecular-mass standards. The samples were analyzed on 7.5% polyacrylamide gels and stained with Coomassie blue
