Fig. 2. RtxA is acylated at lysine residues 558 and 689.
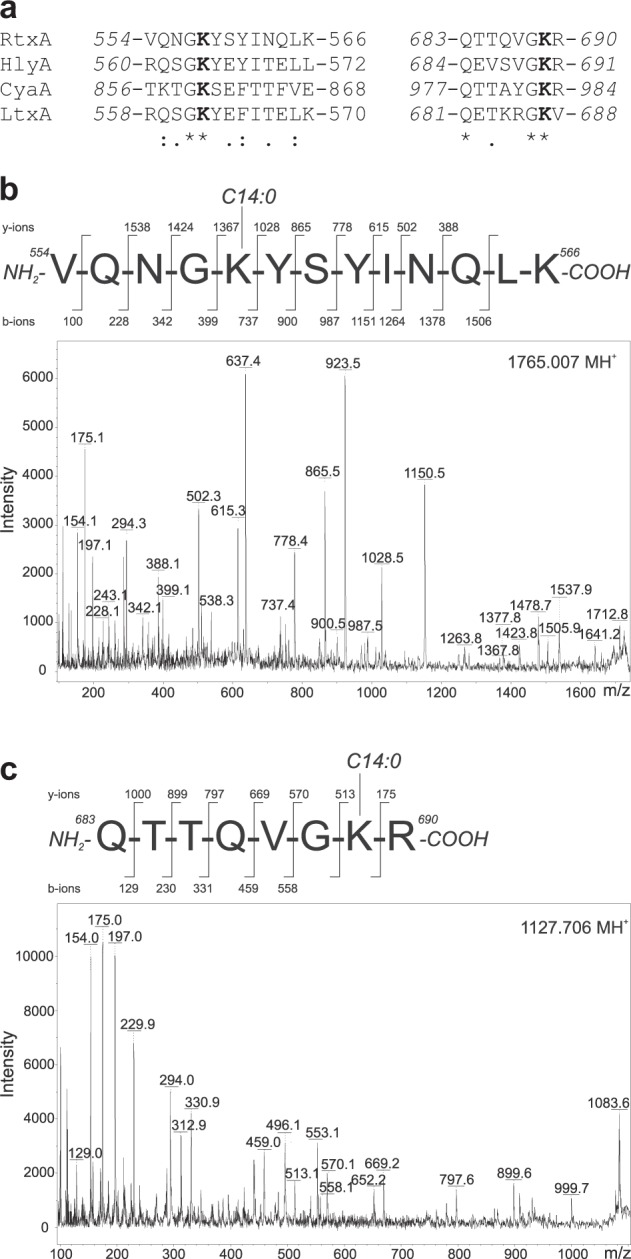
a ClustalW sequence alignment of putative acylated sites of RtxA and corresponding sequences of related RTX toxins whose post-translational modification through amide-linked fatty acylation on the ε-amino group of two conserved internal lysine residues was previously demonstrated:22, 23, 25, 26 RtxA, K. kingae isolate PYKK081 cytotoxin; HlyA, E. coli α-hemolysin (UniProt code: Q8G9Z4); CyaA, B. pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin (UniProt code: P0DKX7); LtxA, A. actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin (UniProt code: P16462). The highly conserved lysine residues (K558 and K689 in RtxA) that have been shown to be acylated in HlyA, CyaA and LtxA are shown in bold. Symbols: (*) identity; (:) strongly similar; (.) weakly similar. b, c The tryptic fragments with m/z signals 1099.675, 1127.706, 1143.699, 1153.723, 1765.007 and 1781.003, which were exclusively present in trypsin-digested RtxA (Supplementary Fig. 1), were further analyzed using a tandem MS/MS sequencing approach. b The MS/MS spectrum of the peptide 1765.007 contains b- and y-ions that correspond to the sequence 554-VQNGKYSYINQLK-566 with the ε-amino group of K558 modified by a myristoyl (C14:0) acyl chain. c The MS/MS spectrum of the peptide 1127.706 contains b- and y-ions that correspond to the sequence 683-QTTQVGKR-690 with a myristoyl (C14:0) acyl group attached to the ε-amino group of K689. The MS/MS spectra of the remaining unexpected peptides (1099.675, 1143.699, 1153.723 and 1781.003) are shown in Supplementary Fig. 2. The residue numbering corresponds to that of the full-length sequence of the RtxA variant from the K. kingae isolate PYKK081
