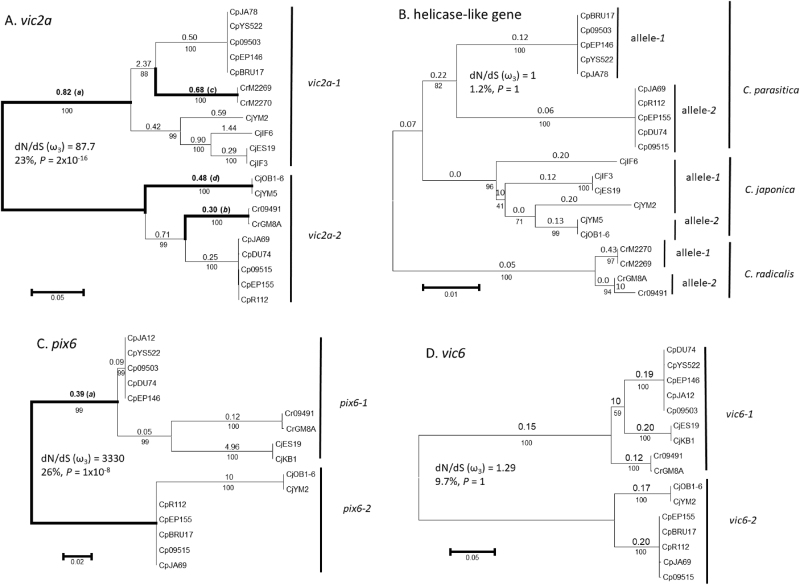
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic trees inferred by maximum likelihood analysis and tests of positive selection on the different branches by branch-site REL and BUSTED analyses. Trees are based on nucleotide sequences from Cryphonectria parasitica (Cp), C. japonica (Cj), and C. radicalis (Cr) for a vic2a, b a helicase-like gene located between vic2 and vic2a, c pix6, and d vic6. Bootstrap values (percentages based on 1000 replications) are shown below branches. Average values of ω ( = dN/dS) are shown above each branch. Branches with significant evidence of positive selection (P ≤ 0.01, branch-site REL) are shown with bold lines and designated by lowercase letters in parentheses (see Table 1 for details). A priori tests for positive selection between alleles 1 and 2 (using BUSTED) are shown for dN/dS (ω3), the percentage of nucleotide sites with evidence of positive selection along the branch contributing to the likelihood ratio significance test and the P-value