FIGURE 1.
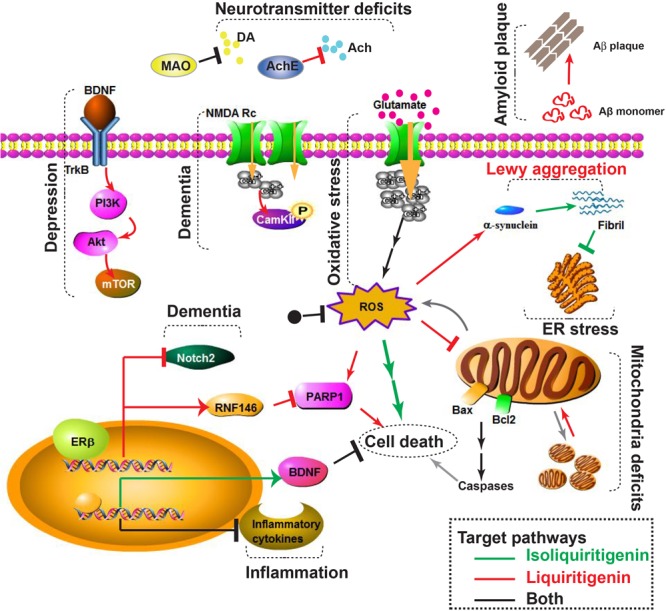
Diagrammatic representation of pathological phenotypes (depression, dementia, inflammation, oxidative stress, amyloid plaque, neurotransmitter deficits, Lewy aggregation, ER stress, mitochondrial deficits, and cell death) and underlying molecular pathways that could be involved in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Pathways regulated by isoliquiritigenin (ILG) and liquiritigenin (LG) were labeled as green and red lines, respectively. Pathways targeted by both ILG and LG were colored as black line. Arrows (↓) denote stimulation and bars (⊥) denote inhibition by ILG (green), LG (red), and both (black). PD related pathways include MAO (monoamine oxidase), and Lewy aggregation. AD related pathways include amyloid plaque formation and AChE (acetylcholine esterase). Other pathological processes are related to both AD and PD, thus could be therapeutic targets by ILG or LG. The scheme was generated by using Pathway Builder Tool.
