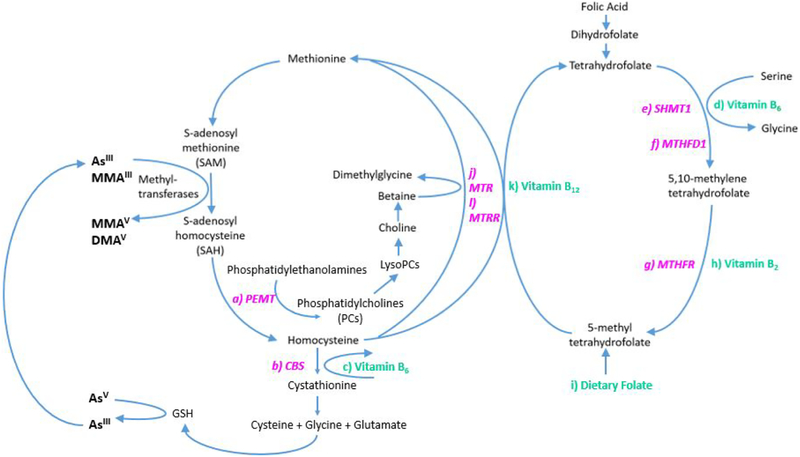
Figure 2. Role of One Carbon Metabolism Related Nutrients and Genes in One Carbon Metabolism Pathway.
Genes are identified in pink and nutrients are identified in green. a) the PEMT gene encodes the PEMT enzyme which converts phosphatidylethanolamine to phosphatidylcholine which supports the remethylation of homocysteine through the choline dependent pathway; b) the CBS gene encodes the CBS enzyme which uses c) vitamin B6 as a co-factor to convert homocysteine into cystathionine; d) Vitamin B6 is also used as a co-factor in the e) SHMT1-catalyzed conversion of tetrahydrofolate to 5,10 methylene tetrahydrofolate; f) the MTHFD1 gene encodes a protein with three enzymatic activities, each involved in the conversion of tetrahydrofolate to 5,10 methylene tetrahydrofolate; g) the MTHFR gene encodes the rate limiting enzyme MTHFR which catalyzes the conversion of 5,10 methylene tetrahydrofolate to 5-methyl tetrahydrofolate using h) vitamin B2, in the form of flavin adenine dinucleotide, as a co-factor; 5-methyl tetrahydrofolate can also enter the one carbon metabolism pathway through intake of i) dietary folate; j) MTR catalyzes the conversion of homocysteine to methionine using k) B12 as a co-factor and 5-methyl tetrahydrofolate as the methyl donor; MTR is reactivated through reductive remethylation by l) MTRR. Abbreviations: CBS (Cystathionine beta synthase); MTHFD1 (Methylenetetrahydrofolate Dehydrogenase); MTHFR (Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase); MTR (Methionine synthase); MTRR (Methionine synthase reductase); PEMT (Phosphatidylethanolamine N-Methyltransferase), SHMT1 (Serine hydroxymethyltransferase)