Figure 1:
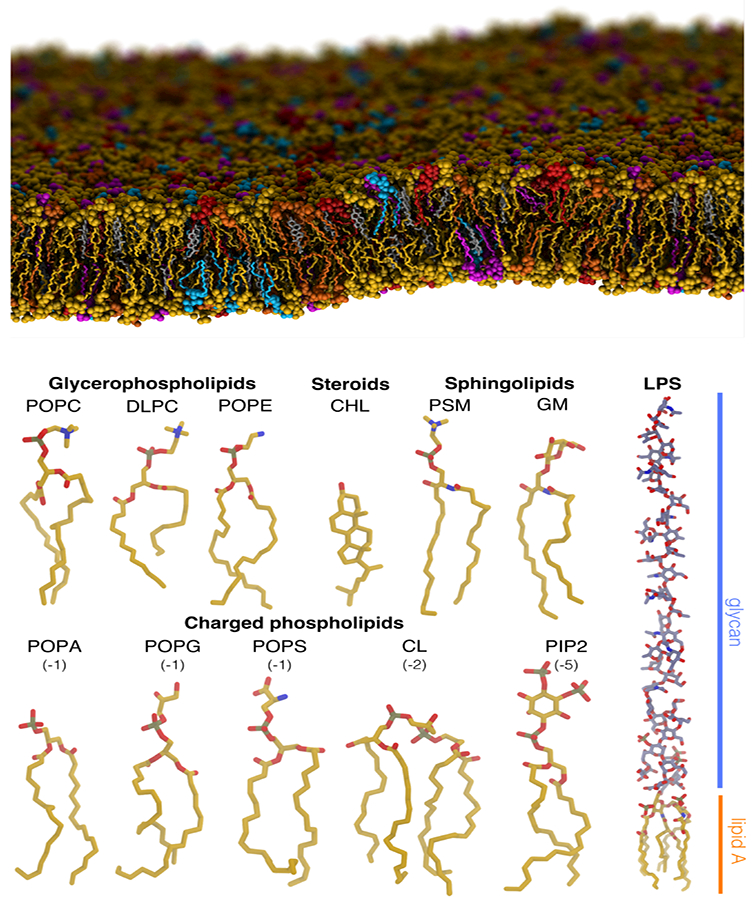
Heterogeneous lipid composition of biological membranes. (Top) An atomistic MD simulation system of a membrane with a complex, heterogeneous lipid composition. Seven different lipids, including cholesterol, cardiolipin, and a variety of phospholipids, are shown in different colors. Spontaneous curvature of the membrane arising from thermal fluctuations in the simulation can be observed. (Bottom) Structures of some exemplary lipids highlighting a variety of important features (e.g., head group charge and size, tail length and saturation, etc.) associated with lipids. Phospholipids and cholesterol (CHL) are major constituents of cellular membranes. Sphingolipids are common signaling lipids, cardiolipins (CL) are essential mitochondrial lipids, and lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are vital bacterial lipids of the outer membrane.
