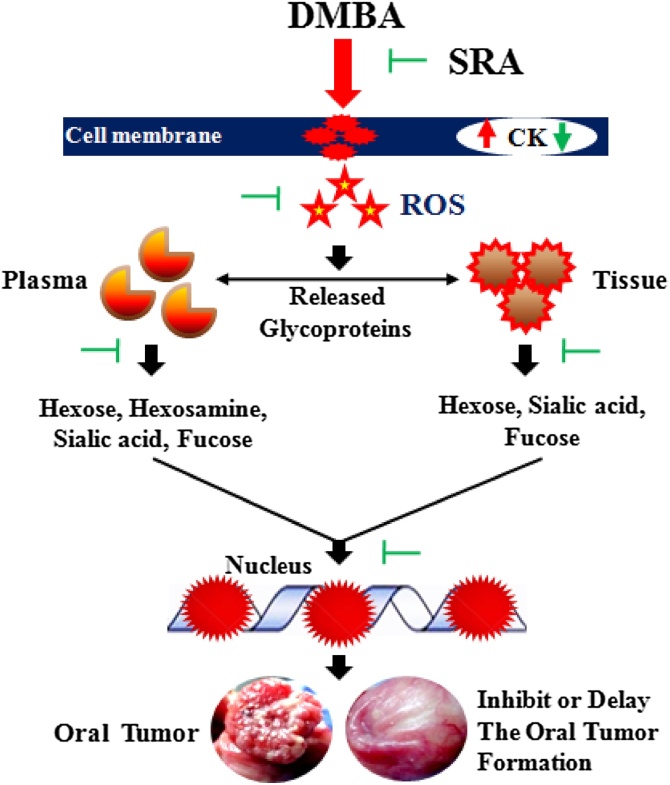
Fig. 8.
Putative action of SRA in DMBA induced cell surface GCs and CK changes in HBPCs.
Pre-administration of SRA (50 mg/kg bw) to DMBA treated suppressed the development of tumor and exhibited moderate keratosis, mild hyperplasia and the expression of CK. SRA inhibited the formation of GPs during neoplastic transformation through altered the activities of glycosylation. Administration of SRA to DMBA induced hamsters, delayed the keratinization of epithelial tissue and prevented cell proliferation. Histological assessment of the GCs expression model in the experimental hamsters interrelated with the biochemical findings. Thus, SRA protects cell surface abnormality in DMBA-induced HBPCs.