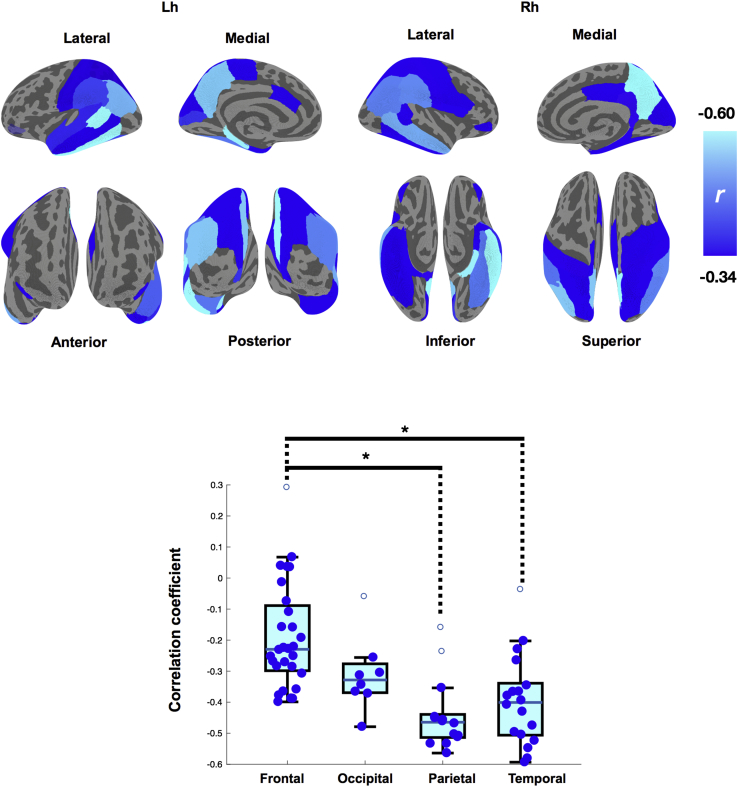
Fig. 4.
The topography of tau-associated brain atrophy. (Top row) Significant local correlations between tau and cortical thickness are overlaid on the cortical surface as parcellated by the Desikan-Killiany atlas (FDR P < .05, data adjusted for age, gender, and scan interval between PET and MRI). The color gradient represents the strength of the negative correlations, increasing in magnitude from dark blue to cyan. (Bottom row) Box plots of correlation coefficients across the major cortical lobes. The degree of local associations was significantly stronger in the temporal and parietal lobes compared with the frontal lobe (Post hoc Tukey-HSD, P < .05). Abbreviations: FDR, false discovery rate; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PET, positron emission tomography.