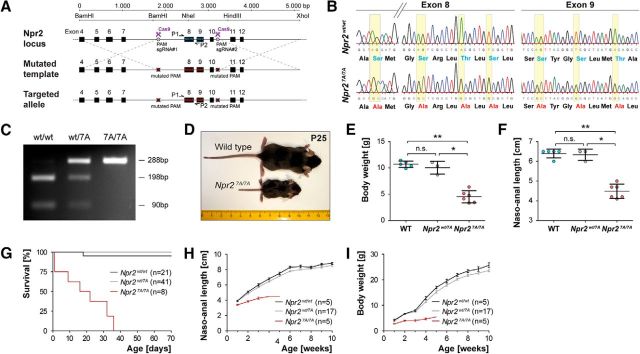
Figure 1.
Generation and validation of the Npr2-7A mouse mutant. A, Targeting strategy for the replacement of seven serine and threonine phosphorylation sites that are encoded in exons 8 and 9 of the murine Npr2 gene by Crispr/Cas9. PAM, Protospacer adjacent motif; sgRNA, synthetic guide RNA. P1 and P2 indicate primer locations for genotyping. B, Sequencing of genomic DNA of the mutated locus in Npr27A/7A and in wild-type, demonstrating the replacement of specific nucleotides in the kinase homology domain. These replacements result in codons, which encode alanine residues instead of serine or threonine residues as indicated below the sequencing information. C, PCR genotyping using primer P1 and P2 followed by digestion with restriction endonuclease NheI, which specifically splits the wild-type sequence but not the mutated segment. D–F, Depiction and quantification of wild-type and Npr27A/7A littermates at postnatal day 25, demonstrating a severely reduced body length and body weight due to impaired endochondral ossification as described previously for other Npr2 loss-of-function mutants. G, Survival rate of Npr27A/7A, Npr2wt/7A, and Npr2wt/wt mice at different ages. Numbers of animals inspected are given in parentheses. H, Naso-anal length of Npr27A/7A, Npr2wt/7A, and Npr2wt/wt male mice at different ages. I, Body weight of Npr27A/7A, Npr2wt/7A, and Npr2wt/wt male mice at different ages. Females are not shown because they were underrepresented in these cohorts, but the same tendency was observed. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.