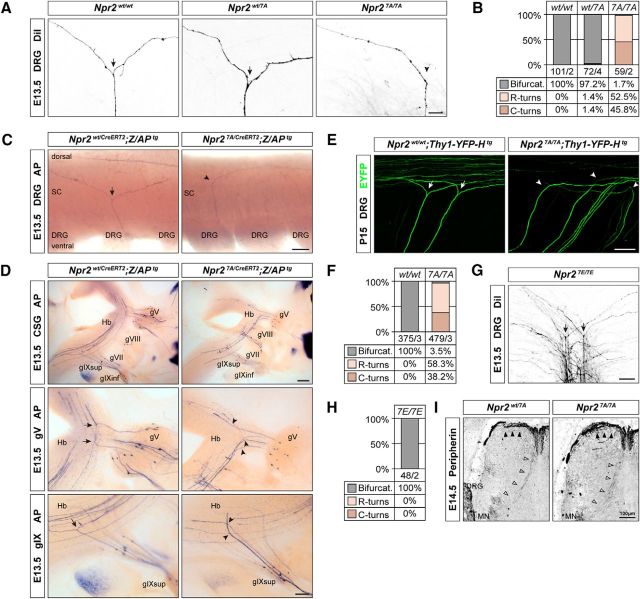
Figure 6.
Axon bifurcation in Npr27A/7A mutants is impaired, whereas axonal branching in Npr27E/7E mutants is normal. A, DiI tracing of DRG axons from Npr27A/7A mutants reveals the absence of bifurcation in the dorsal root entry zone at E13.5. Arrows indicate bifurcation. Arrowhead indicates turn without bifurcation. Scale bar, 25 μm. B, Quantification of branching errors by DiI tracing. Numbers indicate number of axons counted and number of embryos analyzed. C, Alkaline phosphatase stained DRG axons in whole-mount spinal cord preparations from tamoxifen-stimulated Npr2wt/CreERT2;Z/APtg and Npr27A/CreERT2;Z/APtg mice demonstrate loss of axon bifurcation in the spinal cord (SC). Scale bar, 100 μm. D, Lack of bifurcation of axons from cranial sensory ganglion neurons in Npr27A/7A mutant at E13.5 using a genetic approach for sparse labeling of Npr2-positive axons as described previously (Ter-Avetisyan et al., 2014). gV, Ganglion trigeminale; gVII, ganglion geniculi; gVIII, ganglion vestibulare; gIX, ganglion glossopharyngeal superior or inferior; Hb, hindbrain. Scale bar, 200 μm. E, Lack of DRG axon bifurcation in P15 Thy1-YFP-H reporter crossed into Npr27A/7A mutant mice, indicating that compensation does not occur at postnatal stages. Scale bar, 100 μm. F, Quantification of bifurcation errors in the spinal cord using Thy-1-YFP-H reporter mice. G, H, DiI tracing of DRG axons from Npr27E/7E mutants reveals normal sensory axon bifurcation in the dorsal root entry zone at E13.5. Ectopic or repeated bifurcation was not observed, suggesting that permanent responsive Npr2 does not impair bifurcation. Scale bar, 50 μm. I, Collateral formation is not impaired in E14.5 Npr27A/7A mutant mice. Spinal cord cross sections were stained with anti-peripherin. Arrowheads indicate collaterals. MN, Motoneurons. Scale bar, 100 μm.