Figure 4.
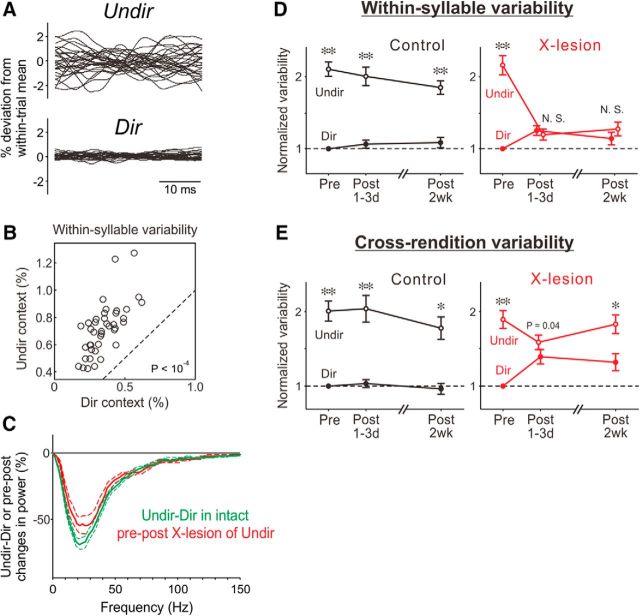
Social context modulation of within-syllable variability depends on Area X. A, Examples of 20 consecutive FF trajectories of a single syllable produced by an intact bird in Undir and Dir contexts show context-dependent modulation of within-syllable FF variability. B, Scatter plots of the magnitude of within-syllable FF variability comparing Undir context with Dir context. Each point corresponds to one syllable. The dashed line indicates unity. p < 10−4. C, Comparison of the effects of social context versus lesions of Area X on within-syllable FF variability. Green, Changes (mean ± SEM) in the power spectrum of FF trajectories from Undir to Dir contexts in intact birds, normalized to the peak height of Undir song spectrum; red, pre–post changes in the power spectrum of Undir song in Area X-lesion birds (data from Fig. 3E replotted for comparison). Conventions are as in Figure 3E. Note the absence of significant differences between Undir–Dir data and Area X-lesion data. D, Within-syllable FF variability in Dir and Undir contexts in control (left) and Area X-lesion (right) birds; variability at all time points and in both contexts were normalized by that of Dir syllables in pre-lesion song. Error bars are SEM. *p < 10−3; **p < 10−4. E, Cross-rendition FF variability in Dir and Undir contexts in control (left) and Area X-lesion (right) birds. Conventions are as in D.