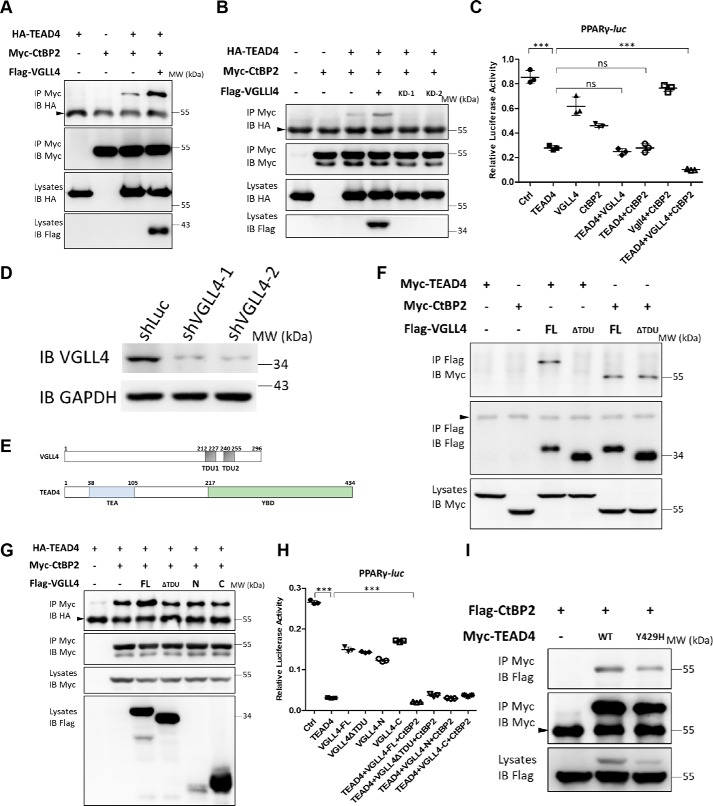
Figure 5.
VGLL4 acts as an adaptor protein to enhance TEAD4–CtBP2 interaction. A, co-IP assay of the interaction between TEAD4 and CtBP2 in the presence or absence of exogenous VGLL4. The indicated plasmids were transfected into 293T cells and analyzed by co-IP. The arrowhead indicates the IgG heavy chain. IB, immunoblot; MW, molecular weight. B, co-IP assay of the interaction between TEAD4 and CtBP2 in the presence or absence of endogenous VGLL4. The indicated plasmids and VGLL4 shRNAs were transfected into 293T cells and analyzed by co-IP. The arrowhead indicates the IgG heavy chain. C, effect of co-expression of TEAD4, VGLL4, and CtBP2 on PPARγ-Luc activity in 293T cells. Data are shown as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). ***, p < 0.001 by Student's t test; ns, no significance. D, immunoblot analysis of shVGLL4–1 and shVGLL4–2 knockdown efficiencies in 293T cells. GAPDH was used as an internal control. The positions of protein molecular mass marker are indicated on the right. E, schematic of the domain organization of human VGLL4 and TEAD4. F, co-IP assay to detect VGLL4 TDU domain function in its interaction with TEAD4 or CtBP2, respectively. The indicated plasmids were transfected into 293T cells and analyzed by co-IP. The arrowhead indicates the IgG heavy chain. FL, full-length. G, co-IP assay to detect the effect of different exogenous VGLL4 truncation forms on the interaction between TEAD4 and CtBP2. The indicated plasmids were transfected into 293T cells and analyzed by co-IP. The arrowhead indicates the IgG heavy chain. H, only VGLL4 full-length could cooperate with TEAD4 and CtBP2 to further inhibit PPARγ-Luc reporter activity. Data are shown as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). ***, p < 0.001 by Student's t test. I, co-IP assay to detect TEAD4Y429 site function in its interaction with CtBP2. The indicated plasmids were transfected into 293T cells and analyzed by co-IP. The arrowhead indicates the IgG heavy chain, and the asterisk denotes the nonspecific band.