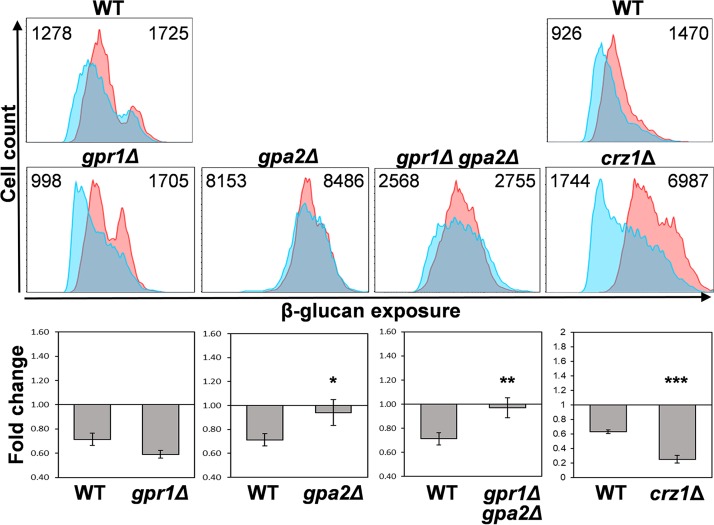
FIG 3.
Hypoxia-induced β-glucan masking is not dependent on Gpr1 or Crz1. Analysis of β-glucan exposure on C. albicans mutants by flow cytometry of Fc-dectin-1-stained cells grown under normoxic (pink) or hypoxic conditions (cyan). The median fluorescence intensity (MFI) for each population is shown at the top right and left of each panel, respectively: WT, wild type, SC5314; gpr1Δ, LR2; gpa2Δ, NM6; gpr1Δ gpa2Δ, NM23; crz11Δ, DSY2195 (Table S1). The wild-type control for each experiment is shown above the mutants examined in that same experiment. The gpr1Δ and gpa2Δ mutants (middle panels) were compared together in the same experiment with the wild-type control (upper left panel), whereas the crz1Δ mutant (middle panel) was compared with wild-type cells in a different experiment (upper right panel). The fold changes in β-glucan exposure for each strain (lower panels) were calculated by dividing the MFI under hypoxic conditions by the MFI for the corresponding normoxic cells. Means and standard deviations from three independent replicate experiments are shown, and the data were analyzed using ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test: *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001.