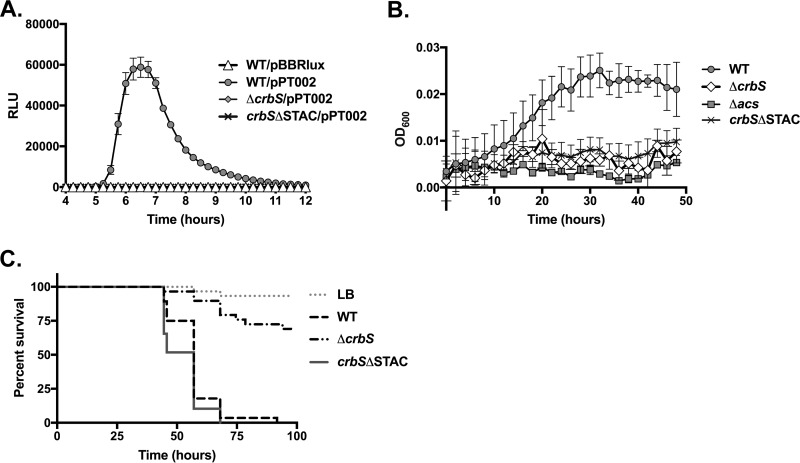
FIG 3.
Effects of the CrbS STAC deletion on acs transcription, acetate metabolism, and fly survival. (A) Deletion of the STAC domain prevents acs promoter activation, similarly to the ΔcrbS strain. For each strain, relative light units (RLU) (defined as luminescence/OD600 unit) from 8 wells of a 96-well plate were measured, with SIO strains carrying either the empty pBBRlux plasmid or the pPT002 plasmid into which the acs promoter was inserted. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (B) Deletion of the STAC domain prevents growth on acetate minimal medium. Growth of the SIO WT, Δacs, ΔcrbS, or crbSΔSTAC strain on M63 minimal medium supplemented with 10 mM acetate was monitored every 2 h for 48 h. Average growth in at least 3 wells of a 96-well plate is shown. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (C) Survival of Drosophila flies infected with the SIO WT, ΔcrbS, or crbSΔSTAC strain. The survival of flies fed the crbSΔSTAC strain did not differ from that of flies fed the WT strain in each of five biological replicates (P > 0.05 by log rank analysis), of which data from one representative experiment are depicted here.