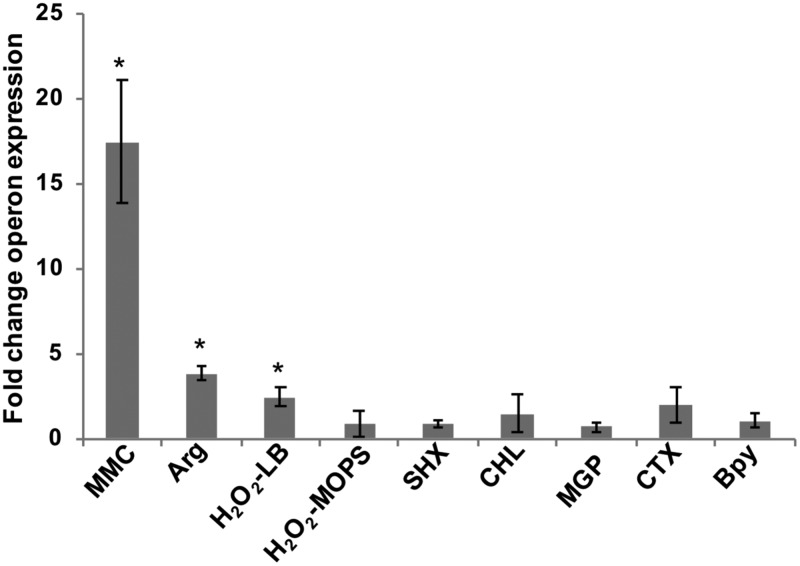
FIG 2.
Expression of the RNA repair operon under conditions that directly or indirectly cause RNA damage. Relative transcript levels for the RNA repair operon were assayed by qRT-PCR for WT S. Typhimurium cultures at mid-log phase, treated versus untreated with the following stress conditions: 3 μM mitomycin C (MMC), 2.5 mM Arg as the sole nitrogen source, 1 mM H2O2 in LB or MOPS minimal medium, 0.4 mg/ml serine hydroxamate (SHX), 30 μg/ml chloramphenicol (CHL), 1% methyl-α-d-glucopyranoside (MGP), 2 μg/ml cefotaxime (CTX), or 250 μM 2,2′-bipyridyl (Bpy). The fold change operon expression is the ratio of normalized operon transcript levels for treated versus untreated samples (*, P < 0.02). For all stress conditions except peroxide stress, rtcA transcript levels were normalized to rpoD transcript levels; for peroxide stress conditions, rtcB transcript levels were normalized to kdgR transcript levels. Data shown are from three biological replicates for each growth condition; error bars represent ±1 standard deviation. The positive control in these qRT-PCR assays was the WT strain containing a multicopy expression vector encoding a constitutively active variant of RtcR (pDS183); the WT(pDS183) strain showed an 83-fold-higher level of rtcA expression than the untreated WT strain (P < 0.01) (these data are not shown in the graph).