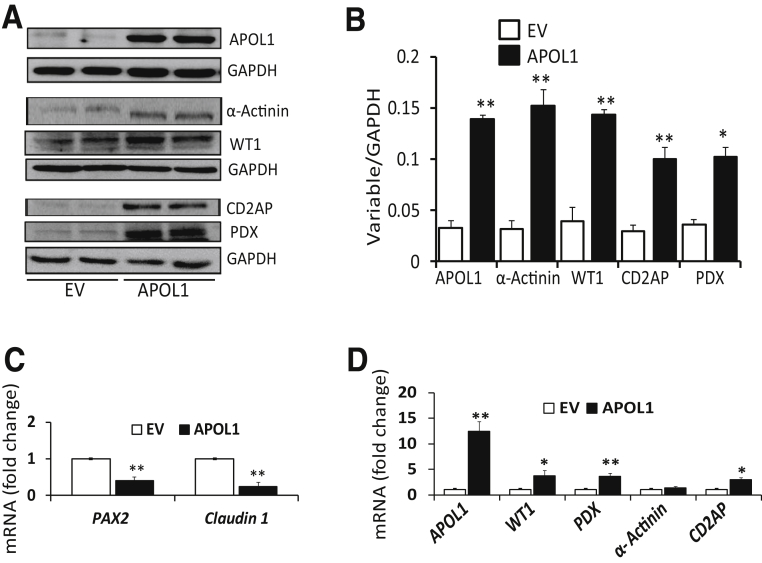
Figure 4.
Induction of apolipoprotein (APOL) 1 expression in human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells induces the expression of transition markers. A: To determine APOL1 induction in kidney cells with undetectable APOL1 protein expression, HEK cells were transfected with empty vector (EV) or APOL1 plasmids. Protein blots were probed for APOL1 and reprobed for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). The same cellular lysates were probed for α-actinin, Wilms' tumor 1 (WT1), CD2AP, and podocalyxin (PDX) and reprobed for GAPDH. Gels from two different lysates are displayed. B: Cumulative densitometric data from the gels generated from the above-mentioned lysates are displayed. APOL1 induction in parietal epithelial cells (PECs) is associated with the expression of transition markers in HEK cells. C: To determine the effect of APOL1 induction on PEC markers in HEK cells, RNAs were extracted from the above-mentioned lysates. cDNAs were amplified for PAX2 and claudin 1. Cumulative data are shown. APOL1 induction in HEK cells down-regulates the transcription of PEC markers. D: To assess the effect of APOL1 induction on PEC transition markers in HEK cells, RNAs were extracted from the above-mentioned lysates. cDNAs were amplified for APOL1, WT1, PDX, α-actinin, and CD2AP. Cumulative data are shown in a bar diagram. The induction of APOL1 in HEK cells is associated with enhanced transcription of transition markers in HEK cells. n = 4 (A). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 versus respective EV.