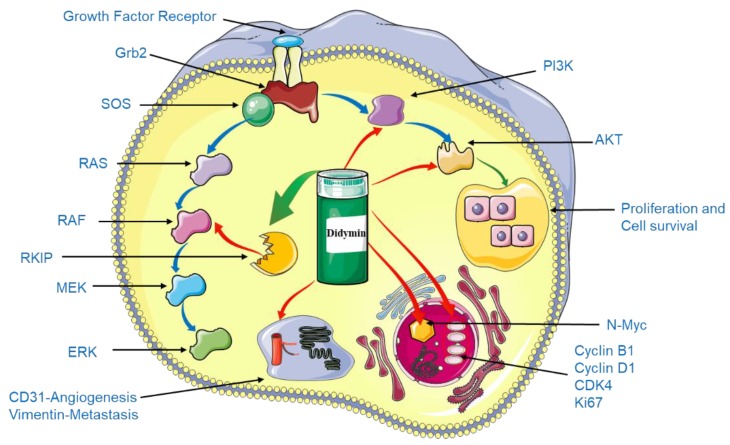
Figure 4.
Didymin affects neuroblastoma signaling pathways. Stimulating the expression of RKIP is a key role for didymin to exert its efficacy. Also, didymin inhibits N-Myc transcription, on the other hand, didymin decreases the expression levels of PI3K, Akt, vimentin, and down-regulates cyclin D1, B1, and CDK4. By staining the pathological sections of the tumor tissue, didymin not only reduced the expression of the angiogenesis marker CD31 in vivo but also inhibited the expression of the proliferation markers Ki67 and N-Myc. The blue arrow indicates normal signal transduction, the green arrow indicates enhancement, and the red arrow represents inhibition.