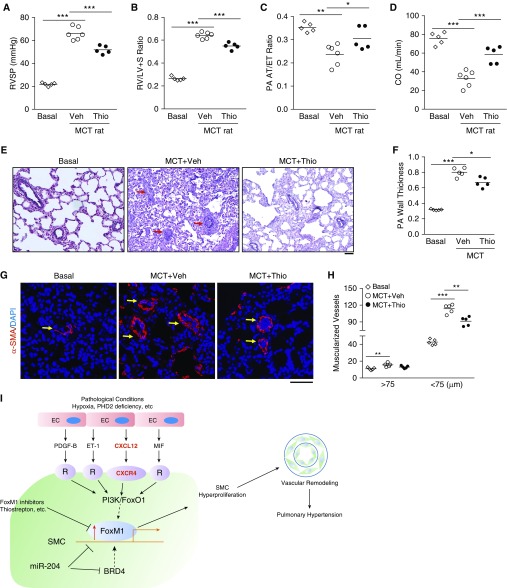
Figure 8.
Thiostrepton (Thio) treatment inhibits monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. (A) Hemodynamic assessment of right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP). Two weeks post-MCT challenge, the rats were treated with either Thio (20 mg/kg, i.p., daily) or vehicle (Veh) for 2 weeks. RVSP was measured at 4 weeks post-MCT challenge. (B) Reduced right ventricular hypertrophy by Thio treatment in MCT rats compared with vehicle-treated MCT rats. (C and D) Echocardiography assessment of pulmonary arterial (PA) acceleration time/ejection time ratio indicating that Thio treatment preserved PA diastolic function and cardiac output. (E and F) Representative micrographs of Russel-Movat pentachrome staining and quantification showing reduced wall thickening in Thio-treated rats compared with vehicle group. Arrows point to PA. PAs with a diameter of 20–200 μm were quantified. (G and H) Muscularization of distal pulmonary vessels reduced by Thio treatment in MCT rats. Sections of rat lung tissues immunostained with anti–α-smooth muscle actin antibody (red). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Arrows indicate muscularized distal pulmonary vessels. (I) A scheme showing the concept that upregulation of FoxM1 expression in smooth muscle cells (SMCs) induced by endothelial cell (EC)-derived factors through EC-SMC crosstalk mediates SMC proliferation leading to pulmonary vascular remodeling and development of pulmonary hypertension. Under various pathologic conditions (e.g., hypoxia and PHD2 deficiency) ECs release multiple paracrine factors, such as PDGF-B, ET-1, CXCL12, and MIF, which act to induce FoxM1 expression in SMCs likely through PI3K/FoxO1 signaling; activation of FoxM1 in SMCs results in SMC proliferation, which leads to pulmonary vascular remodeling and pulmonary hypertension. Other studies also show BRD4 and miR-204 regulates FoxM1 expression in SMCs. Thus, pharmacologic inhibition of FoxM1 may represent a novel therapeutic strategy to inhibit pulmonary vascular remodeling for treatment of IPAH. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. (A–D, F, and H) One-way ANOVA. Scale bars: (E) 100 μm; (G) 50 μm. CO = cardiac output; FoxM1 = forkhead box M1; PA AT/ET = pulmonary arterial acceleration time/ejection time; R = receptor; RV/(LV + S) = right ventricle versus left ventricle plus septum; SMA = smooth muscle actin.