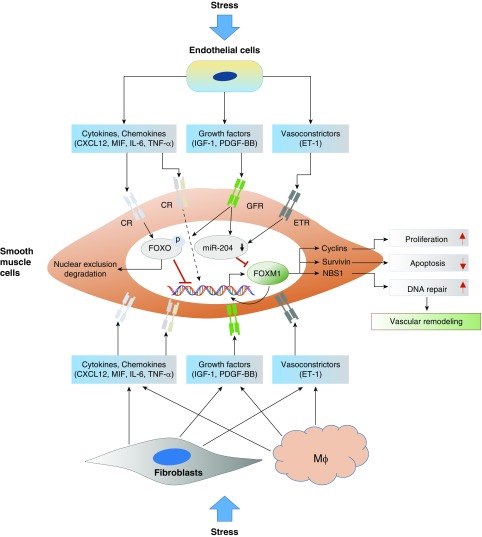
Figure 1.
Role of Fox (forkhead box) transcription factors in pulmonary hypertension. Numerous stresses can activate pulmonary vascular cells including endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and resident and recruited macrophages. Activated vascular cells produce increased amounts of cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, and vasoconstrictors, leading to increased FoxM1 gene expression in smooth muscle cells via reduced FoxO activity, which is a negative transcriptional regulator of FoxM1 gene expression; reduced levels of miR-204, also a negative regulator of FoxM1 mRNA stability and translation; and open FoxM1 chromatin structure, via phosphorylating histones and epigenetic regulators by signal-activated kinases. Increased FoxM1 levels and activity result in smooth muscle cell proliferation, apoptosis resistance, and genome stability by activating genes involved in cell proliferation, antiapoptosis, and DNA repair. CR = cytokine receptor; CXCL12 = chemokine ligand 12; ET-1 = endothelin-1; ETR = endothelin receptor; GFR = growth factor receptor; IGF-1 = insulin-like growth factor-1; Mϕ = macrophage; MIF = macrophage migration inhibitory factor; NBS1 = Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1; PDGF-BB = platelet-derived growth factor-BB; TNF-α = tumor necrosis factor-α.