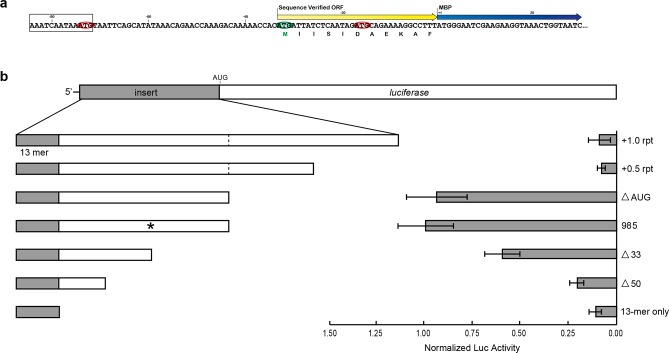
Figure 4.
Characterization of sequence constraints for a 13-mer motif. (a) Identification of authentic translation initiation sites by protein sequencing of in vitro-expressed MBP from the high-activity TEE HGL6.985. The protein sequence is listed below the nucleotide sequence. Color scheme: 13-mer motif (black box), MBP coding region (blue arrow), authentic translation initiation site (yellow arrow), and AUG triplets in-frame and out-of-frame with the MBP coding region (green and red ovals, respectively). (b) Mutational analysis of HGL6.985. Modifications were made to increase the 5′ leader length through addition of both a half-repeat and a full repeat (+0.5 rpt and +1.0 rpt, respectively) of the HGL6.985 sequence. A decrease in sequence length was achieved by removal of 33 (Δ33), 50 (Δ50), and all of the nucleotides downstream of the 13-mer motif (13-mer only). The authentic initiation site (*) within the TEE sequence was also deleted through mutation (ΔAUG). The functional impact of each mutation was assessed by measuring luciferase expression levels in HeLa cells relative to the unmodified HGL6.985 sequence and normalized to luciferase mRNA levels. Error bars designate the standard deviation.